피부관리실 내부마케팅이 직원의 직무만족에 미치는 영향- 빛채 그룹을 중심으로 -
The Effect of Esthetic Salon's Internal Marketing on Employee's Job Satisfaction – Focus on Be-chae Group -
Article information
Trans Abstract
The purpose of this study is to analyze the effects of esthetic salon's internal marketing factors on the employees' job satisfaction, seek continuous internal marketing strategies in order to enhance esthetic business' internal customer satisfaction, improve the esthetic salon's service competitiveness, and use the study results as baseline data for the esthetic industry development. This study targeted skin specialists working in three brand companies of Be-chae Group, namely Yakson House, Dalia Spa, and Yeorihan Diet by region. The internal marketing factors were divided into six factors: welfare, communication, management's support, authority delegation, and reward system. The findings in this study are as follows: First, for differences in internal marketing factors according to general characteristics, men's overall recognition was higher than women's. The participants in their 30s showed higher recognition of communication than those in their 20s. The married people's recognition of communication and reward system was higher than the unmarried people's. by company, the recognition of the internal marketing factors was the highest in the following order: Dalia Spa, Yeorihan Diet, and Yakson House. By working region, Chungcheong Province's recognition of the internal marketing factors was higher than other regions’, which is connected to its higher job satisfaction than in other regions. Directors' recognition of the internal marketing factors than other employees' was higher and the employees who worked less than one year and over five years showed higher recognition of the internal marketing factors. No significant differences depending on education, major before joining the companies, and residential type were shown. Second, men, married people, Dalia Spa and Yeorihan Diet, directors, Chungcheong Province, and employees working less than one year and over five years showed relatively higher job satisfaction according to general characteristics. From this, it was found out that the participants' job satisfaction was higher as recognition of the internal marketing factors was higher. No significant differences depending on age, education, major before joining the companies, and residential type were shown. Third, the reward system factor was the highest between the internal marketing factors and job satisfaction as a result of the correlation analysis, followed by management's support, welfare, education/training, authority delegation, and communication in order. Therefore all the sub-factors of the internal marketing were important to the employees' job satisfaction. Based on the findings, this study expects esthetic companies to continuously perform management strategies using the internal marketing factors and place corporate culture to improve the employees' job satisfaction. The consolidation of esthetic salon employees' competitiveness is expected to be connected to external customer satisfaction, which is expected to be linked to the skin care industry's development.
I. 서 론
최근 기업들은 급변하는 경영환경과 새로운 유형의 경쟁업체의 출현과 소비자 요구의 다양화로 인한 생존시장에서 경쟁적 우위를 차지하기 위해 기업의 환경과 조직 특성에 맞는 전략을 수립하면서 생존경영을 이어나가고 있다. 서비스기업은 외부고객과 기업의 종사원인 내부고객, 두 종류의 고객을 갖고있다. 외부고객에게 상품을 판매한다면 내부고객에게는 업무를 판매한다. 종사원은 ‘그들 자체가 서비스’이기 때문에 서비스기업에서 매우 중요한 역할을 한다(Lee, 2008). 특히, 미용서비스업은 다른 업종에 비해 종사원이 고객과의 접촉 시간이 길고 미용서비스의 특성상 종사원의 기술로써 제품화되는 무형성, 동일 고객이라도 종사원의 수행능력에 따라 서비스 품질이 다르게 나타나는 이질성, 서비스가 저장될 수 없는 소멸성, 고객 상담 후 관리가 이루어지는 생산과 소비가 동시에 발생하는 비분리성으로 대량생산이 어렵기 때문에 인적 서비스가 이상적으로 제공되어야 매출과 수익을 창출할 수 있다(Song, 2008). 미용서비스에 있어서 고객만족은 종사원의 행위나 태도에 의해 크게 좌우되므로 고객만족 이전에 종사원 만족이 선결되어야 하는데 이러한 배경에서 등장한 개념이 내부고객지향의 내부마케팅 개념이다(Lee, 2013). 내부마케팅이란 직원을 최초의 고객으로 여기고 서비스 마인드나 고객 지향적 사고를 심어주어 더 좋은 성과를 낼 수 있도록 동기부여 하는 활동이며 일종의 경영전략으로 이해할 수 있다(Lee, 2008).
Lee(2015)의 연구결과에 따르면 서울·경기지역 프랜차이즈 미용실 대상으로 조사한 결과 내부마케팅의 커뮤니케이션, 보상시스템 요인 순서로 직무만족에 영향을 미치는 것으로 나타났고, Lee(2007)의 연구결과에서 서울시 구청 공무원 대상으로 직무만족에 가장 많은 영향을 미치는 내부마케팅 요인은 내부커뮤니케이션, 교육훈련으로 나타났으며 Seo(2013)의 연구결과에서 서울지역 종합병원 직원 대상으로 조사한 결과 커뮤니케이션, 권한위임, 보상제도에 대한 평가가 높을수록 종사자의 직무만족이 높아지는 것으로 나타났다. Bae(2017)의 연구결과에서는 외식업 종사자 대상으로 조사한 결과 경영층지원이 내재적, 외재적 직무만족에 긍정적 영향을 미치는 것으로 나타났고, Shim(2019)의 연구결과에서는 서울지역 호텔 종사자 대상으로 조사한 결과 업무지원, 커뮤니케이션이 직무만족에 긍정적 영향을 미치는 것으로 나타났으며 Hwang(2016)의 연구결과에서는 항공사 객실 승무원 대상으로 조사한 결과 내부커뮤니케이션과 권한위임 순서로 직무만족에 영향을 미치는 것으로 나타났다. 본 연구에서는 선행연구를 참고하여 내부마케팅요인으로 검증된 복리후생, 커뮤니케이션, 경영진의 지원, 권한위임, 교육훈련, 보상제도 6가지 하위요인으로 적용하였다. 다양한 분야에서 내부마케팅 요인에 따른 종사원의 직무만족에 대한 연구가 진행되어지고 있으나 피부관리실 종사원 대상으로의 연구는 너무나 미흡한 상태이다.
이에 본 연구는 피부관리실 내부마케팅 요인이 종사원의 직무만족에 미치는 영향을 분석하여 피부미용업체의 내부고객만족을 높이는 기업문화 정착과 서비스경쟁력을 높이기 위한 마케팅전략 수립에 도움이 되고자 한다.
II. 이론적 배경
1. 내부마케팅의 개념
내부마케팅이란 서비스기업의 첫 번째 시장은 종사원이라는 관점에서 고객보다 앞서 종사원에게 서비스가 제공하려는 편익을 알리고 설득하고 교육시켜 내부시장의 욕구를 먼저 충족시키는 활동으로(George, 1990) 기업이 종사원을 대상으로 하는 마케팅 활동이다(Gronroos, 1990).
1) 복리후생
조직이 구성원과 그의 가족들을 대상으로 하여 신체적, 정신적, 경제적으로 직접 또는 간접적으로 보상하여 복지를 행하는 일체의 제도이며(Choi, 2013) 기업이 구성원의 생활수준, 복지향상을 위해 기본적 근로조건 이외에 제공하는 부가적인 지급을 의미한다(Leeg, 2007).
2) 커뮤니케이션
조직 구성원 상호간 의사소통을 통해 꾸준한 정보교환 활동을 가능하게 하는 것으로(Kim, 2018) 기업의 사업계획, 의사결정 내용 등 중요 정보를 공유함으로써 구성원 간의 신뢰감 형성과 종사원 스스로 자신감을 바탕으로 고객서비스 시 유연성 있게 대처해 나갈 수 있다(Lee, 2012).
3) 경영진의 지원
경영자에게 종사원들의 접근이 쉬운 조직 분위기를 조성하고, 조직 활동에서 종사원을 계획에 참여시키며 기업 내부 지침이나 개방된 커뮤니케이션 등 경영자가 종사원에게 관심을 가져주어 조직의 의사결정 과정에 종사원을 참여시키는 활동이다(Lukas & Maignan, 1996).
4) 교육훈련
기업의 전략적 목표 달성을 위해 종사원의 지식과 기능을 향상시키고, 조직의 사명과 전략에 대한 이해를 도와 맡은 바 직무를 효과적으로 수행할 수 있도록 지원하기 위해 계획된 기업의 조직적인 활동이다(Yoon, 2009).
5) 권한위임
직접적으로 서비스를 제공하고 있는 종사원에게 가능한 최대의 의사결정권을 부여하여 업무과정에서 문제해결 시 신속한 의사결정으로 대처할 수 있는 도구로(Berry, 1995) 종사원의 태도와 행위변화를 유도하여 직무만족을 증대시킬 수 있다(Seo, 2013).
6) 보상제도
기업이 내부고객에게 최상의 품질을 제공하기 위하여 종사원의 조직 내 다양한 노력에 대하여 포상하는 제도로서 종사원이 기업에 노동력을 제공하고 그 대가로 받게 되는 임금, 상여금, 복리후생 등을 모두 포함하는 포괄적인 개념이다(Park, 2016).
2. 직무만족의 개념
Smith(1955)는 조직구성원 개인이 자신의 직무를 실행하면서 경험하게 되는 모든 감정의 전체 그리고 감정의 균형 상태에서 발생하게 되는 일련의 태도라고 하였다. 기업의 내적 측면에서 직무만족이 중요한 것은 구성원의 직무만족은 사업성과에 영향을 주며 기업에 대한 긍정적인 평가를 공유하며 조직외부와 내부에 우수한 인간관계를 유지해 나가며 이직률 감소와 생산성 향상을 이루기 때문이다(Kim, 2012).
직원의 만족 유형을 일, 직장, 인사, 근로조건, 회사에 대한 만족으로 하였으며(Lee, 2008) 내부마케팅의 목표가 직원의 직무만족 향상이므로 기업성장을 위해 매우 중요한 개념이라 할수 있다. 직무만족이란 종사원의 직무에 대한 태도의 하나로서 종사원 스스로가 직무나 직무경험을 평가한 결과에서 얻어지는 즐겁고 긍정적인 정서의 상태(Locke, 1976)라고 정의 할 수있다.
III. 내용 및 방법
1. 연구대상 및 자료수집
본 연구의 조사대상은 피부관리실 종사자로서 빛채그룹 직원을 대상으로 하였고, 자료수집 방법으로는 자기 기입식 설문지법이 사용되었다. 본 조사는 2020년 12월 14일부터 24일까지 예비조사를 거쳐 12월 28일부터 2021년 1월 6일까지 본 조사를 실시하였다. 총 470부의 설문지를 배부하여 전체 회수하였고 465부의 유효 설문지로 통계를 내어 최종분석 자료로 사용 되었다.
2. 연구방법
선행연구를 참고한 설문지 구성은 다음과 같다. 일반적 사항으로 10문항이며 내부마케팅은 Seo(2013), Lim(2012)의 연구를 참고로 복리후생, 커뮤니케이션, 경영진의 지원, 교육훈련,권한위임, 보상제도 6가지 요인으로 27문항으로 구성하였고 직무만족은 Lee(2007), Kim(2016)의 연구에서 사용된 설문문항을 수정 보완하여 8문항으로 하여 총 45문항으로 구성하였다.
수집된 자료의 통계처리는 SPSS WIN 21.0 프로그램을 사용하여 분석하였다. 첫째, 조사대상자의 일반적 특성에 대해 알아보기 위하여 빈도분석을 실시하였다. 둘째, 측정도구의 타당도 분석을 위해 탐색적 요인분석을 실시하였고, 신뢰도 분석을 위해 Cronbach's α계수를 사용하였다. 셋째, 피부관리실 내부마케팅 요인과 직원의 직무만족에 대해 알아보기 위하여 기술통계분석을 실시하였고, 조사대상자의 일반적 특성에 따라 차이가 있는지를 알아보기 위하여 독립표본 t-test 및 일원변량분석(One way ANOVA)을 실시하였으며, 사후검정 방법으로는 Scheffé test를 실시하였다. 넷째, 각 변수들 간의 상관관계를 알아보기 위하여 상관관계분석을 실시하였다. 다섯째, 피부관리실 내부마케팅 요인이 직원의 직무만족에 미치는 영향을 알아보기 위하여 다중회귀분석을 실시하였다.
IV. 결과 및 고찰
1. 조사대상자의 일반적 특성
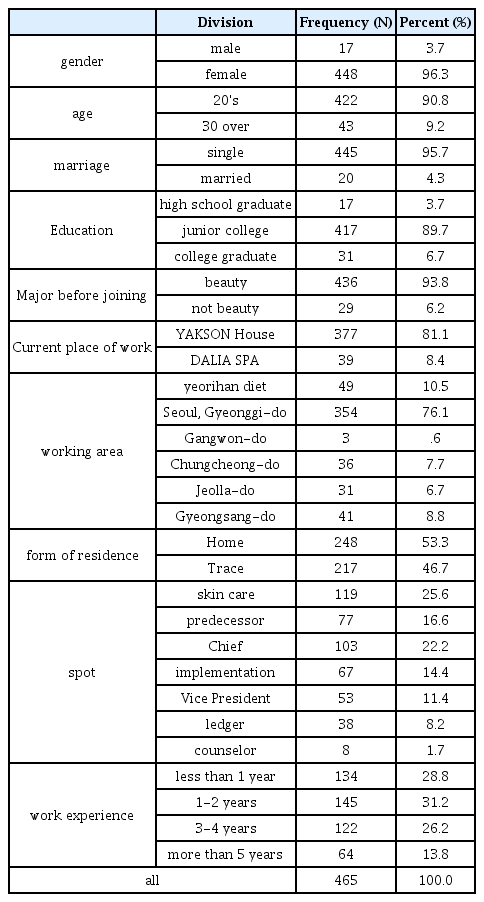
조사대상자의 일반적 특성에 대해 알아보기 위하여 빈도분석을 실시한 결과는 <Table 1>과 같다. 성별은 여성 448명(96.3%), 남성 17명(3.7%)이며 연령은 20대 422명(90.8%), 30대 이상 43명(9.2%)이며 결혼은 미혼 445명(95.7%), 기혼 20명(4.3%)이며 학력은 고졸 17명(3.7%), 전문대학 417명(89.7%),학사 이상 31명(6.7%)이며 입사 전 전공은 미용 436명(93.8%), 미용아님 29명(6.2%)이며 현재 근무처는 약손명가 377명(81.1%), 여리한 다이어트 49명(10.5%), 달리아 스파 39명(8.4%) 순으로 나타났다.
근무 지역은 서울·경기도 354명(76.1%), 경상도 41명(8.8%), 충청도 36명(7.7%), 전라도 31명(6.7%), 강원도 3명(0.6%) 순으로 나타났고, 거주 형태는 자택 248명(53.3%), 자취 217명(46.7%)이며 직위는 피부관리사 119명(25.6%), 전임 77명(16.6%), 주임 103명(22.2%), 실장 67명(14.4%), 부원장 53명(11.4%), 원장 38명(8.2%), 상담사 8명(1.7%)이며 근무 경력은 1년 미만 134명(28.8%), 1-2년 145명(31.2%), 3-4년 122명(26.2%), 5년 이상 64명(13.8%)으로 나타났다.
2. 측정도구의 타당성 및 신뢰도 검증
측정 도구의 타당도를 검증하기 위해 탐색적 요인분석(Exploratory factor analysis)을 실시하였다. 요인분석 방법 중원래의 변수들의 분산 중 가급적 많은 부분을 설명하는 요인을 추출하면서 정보손실을 최소화하는 주성분분석(Principal component analysis)을 사용하였고, 요인의 독립성을 유지하면서 요인 구조가 가장 뚜렷할 때까지 요인을 회전시키는 베리맥스 회전(Varimax rotation)을 사용하여 분석하였다. 신뢰도 검증을 위해서는 Cronbach's α계수를 산출하여 개별항목과 전체 항목에 대한 신뢰성을 평가하는 내적 일관성 검증법을 사용하였다. 일반적으로 Cronbach's α계수가 0.60 이상이면 신뢰성이 있다고 보며 전체 변수(항목)를 하나의 척도로 종합하여 분석할 수 있다.1)
1) 내부마케팅 요인에 대한 타당성 및 신뢰도 검증
내부마케팅 요인에 대한 타당성 및 신뢰도 검증 결과는 <Table 2>와 같다. 요인분석 결과에 의하면 KMO 측도는 0.960으로 높게 나타났고, Bartlett의 구형성 검정 결과 χ²=13674.596(p<.001)으로 적절한 것으로 분석되었다. 고유값(Eigen values)을 토대로 6개 요인을 추출하였으며 전체 설명력은 81.531%로 나타나 요인 1(18.192%)은 ‘복리후생’, 요인 2(15.445%)는 ‘교육훈련’, 요인 3(14.372%)은 ‘보상제도’, 요인 4(12.952%)는 ‘경영진 지원’, 요인 5(10.344%)는 ‘권한위임’, 요인 6(10.225%)은‘커뮤니케이션’으로 명명하였다. 6개 요인의 요인 적채치는 모두 0.40 이상으로 나타나 타당성이 검증된 것으로 볼 수 있고, 신뢰도 또한 0.60 이상으로 나타나 신뢰할만한 수준으로 볼 수있다.
2) 직무만족에 대한 타당성 및 신뢰도 검증
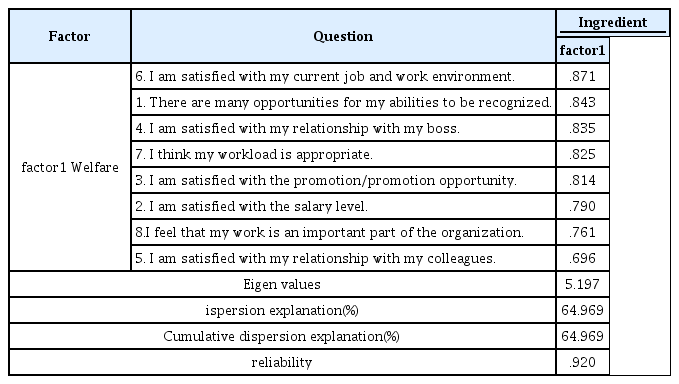
직무만족에 대한 타당성 및 신뢰도 검증 결과는 <Table 3>과 같다. 요인분석 결과에 의하면 KMO 측도는 0.920으로 높게 나타났고, Bartlett의 구형성 검정 결과 χ²=2470.111(p<.001)로 적절한 것으로 분석되었다. 고유값(Eigen values)을 토대로 1개 요인을 추출하였으며 전체 설명력은 64.969%로 나타났다. 즉, 요인 1(64.969%)은 ‘직무만족’으로 명명하였다. 1개 요인의 요인 적채치는 모두 0.40 이상으로 나타나 타당성이 검증된 것으로 볼 수 있고, 신뢰도 또한 0.60 이상으로 나타나 신뢰할만한 수준인 것으로 볼 수 있다.
3. 기술통계적 분석
다음은 피부관리실 내부마케팅 요인과 직원의 직무만족에 대해 알아보고, 조사대상자의 일반적 특성에 따라 차이가 있는지를 알아보기 위하여 독립표본 t-test 및 일원변량분석(One way ANOVA)을 실시한 결과이다. 사후검정 방법으로는 Scheffé test를 실시하였다.
1) 피부관리실 내부마케팅 요인
(1) 전반적인 피부관리실 내부마케팅 요인
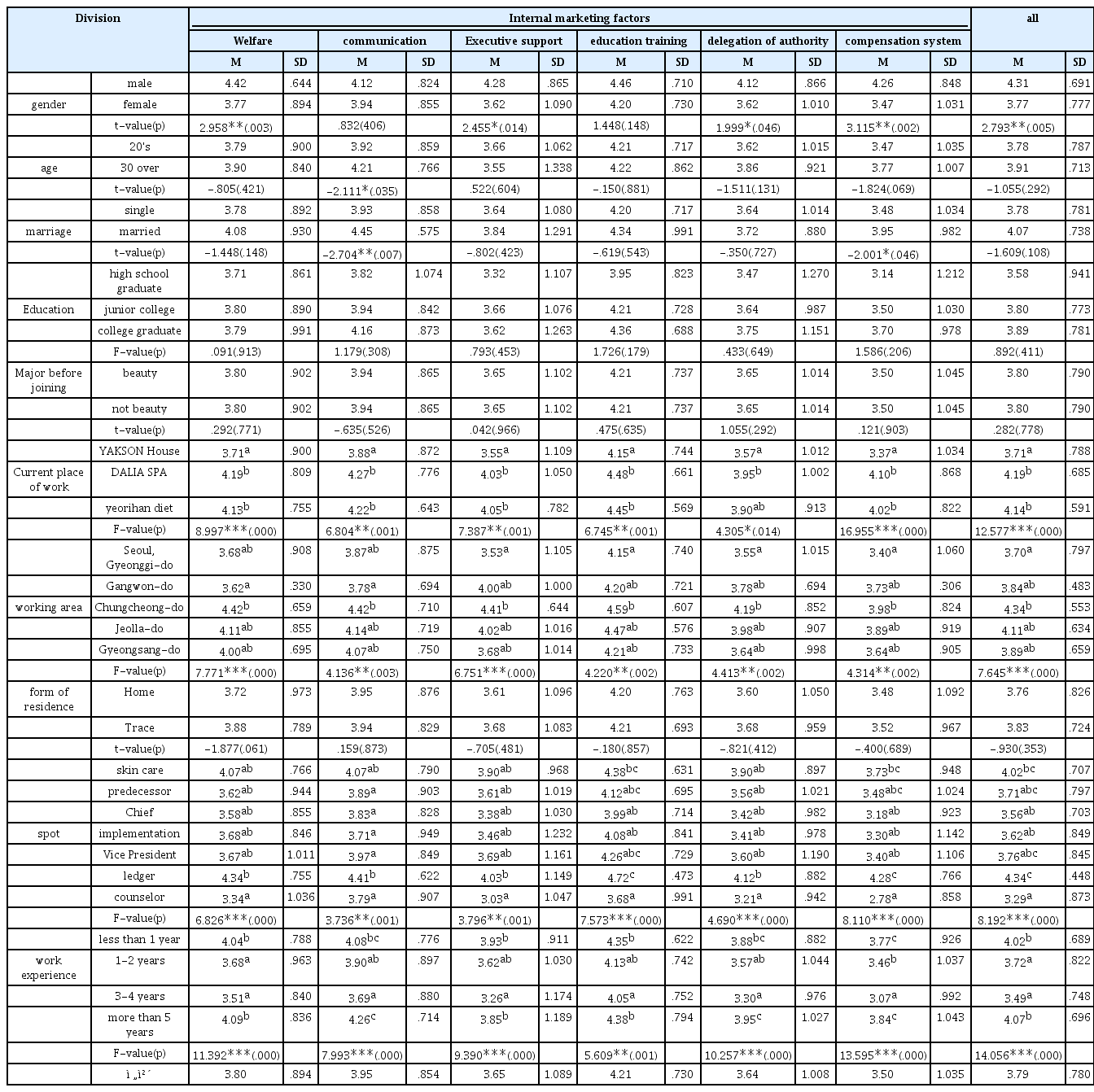
전반적인 피부관리실 내부마케팅 요인에 대해 알아보기 위하여 기술통계분석을 실시한 결과는 <Table 4>와 같다. 분석결과 전체적으로 볼 때, ‘교육훈련’(M=4.21)이 가장 높게 나타났고, ‘커뮤니케이션’(M=3.95), ‘복리후생’(M=3.80), ‘경영진 지원’(M=3.65), ‘권한위임’(M=3.64), ‘보상제도’(M=3.50) 순으로 나타났으며, 전반적인 피부관리실 내부마케팅 요인은 평균 3.79점으로 나타났다.
(2) 일반적 특성에 따른 피부관리실 내부마케팅의 차이
일반적 특성에 따라 피부관리실 내부마케팅 요인에 차이가 있는지를 분석한 결과는 <Table 5>와 같다. 분석결과 성별에 따라서 통계적으로 유의미한 차이가 나타났으며(p<.05) 남성의 경우 여성에 비해 상대적으로 전반적인 내부마케팅 요인과 하위요인별 복리후생, 경영진 지원, 권한위임, 보상제도 인식이 높은 것으로 나타났다. 연령에 따라서는 통계적으로 유의미한 차이가 나타났으며(p<.05), 20대에 비해 30대 이상의 경우 상대적으로 커뮤니케이션 인식이 높은 것으로 나타났다.
결혼에 따라서는 내부마케팅 요인의 하위요인별 커뮤니케이션, 보상제도에 대해 통계적으로 유의미한 차이가 나타났으며(p<.05), 기혼의 경우 미혼에 비해 상대적으로 커뮤니케이션,보상제도 인식이 높은 것으로 나타났다. 현재 근무처에 따라서는 통계적으로 유의미한 차이가 나타났으며(p<.05), 달리아 스파, 여리한 다이어트, 약손명가 순으로 내부마케팅 요인 인식이 높게 나타났는데 빈도수와 반비례 현상으로 나타난 것으로 여겨진다. 특히 달리아 스파는 복리후생, 커뮤니케이션, 교육훈련, 권한위임, 보상제도 5개 요인에서 인식이 가장 높게 나타났고 여리한 다이어트는 경영진지원 요인에서 인식이 가장 높게 나타났으며 약손명가는 6개요인 모두 인식이 가장 낮게 나타났다. 근무 지역에 따라서는 통계적으로 유의미한 차이가 나타났으며(p<.01), 충청도 지역의 경우 타 지역에 비해 상대적으로 전반적인 내부마케팅 요인과 하위요인별 복리후생, 커뮤니케이션, 경영진 지원, 교육훈련, 권한위임, 보상제도 인식이 높은 것으로 나타났는데 직무만족도 또한 타 지역보다 높게 나타난 것과 연관되어 진다. 직위에 따라서는 통계적으로 유의미한 차이가 나타났으며(p<.01), 원장의 경우 타 직위에 비해 상대적으로 전반적인 내부마케팅 요인과 하위요인별 복리후생, 커뮤니케이션, 경영진 지원, 교육훈련, 권한위임, 보상제도 인식이 높은 것으로 나타났다. 근무 경력에 따라서는 통계적으로 유의미한 차이가 나타났으며(p<.01), 1년 미만이나 5년 이상의 경우 1-2년이나 3-4년에 비해 상대적으로 전반적인 내부마케팅 요인과 하위요인별 복리후생, 커뮤니케이션, 경영진 지원, 교육훈련, 권한위임, 보상제도 인식이 높은 것으로 나타났다.
이 외에 학력, 입사 전 전공, 거주 형태에 따라서는 통계적으로 유의미한 차이가 나타나지 않았다(p>.05).
2) 직무만족
(1) 전반적인 직무만족
전반적인 직무만족에 대해 알아보기 위하여 기술통계분석을 실시한 결과는 <Table 6>와 같다. 분석결과 전반적인 직무만족은 평균 3.75점으로 나타났다.
(2) 일반적 특성에 따른 직무만족 차이
일반적 특성에 따라 직무만족에 차이가 있는지를 분석한 결과는 <Table 7>과 같다. 분석결과 성별, 결혼은 통계적으로 유의미한 차이가 나타났으며(p<.05), 현재 근무처, 근무 지역, 직위, 근무 경력에 따라 통계적으로 유의미한 차이가 나타났다(p<.001). 성별에서는 여성에 비해 남성이, 결혼에서는 미혼에 비해 기혼이, 근무처에서는 약손명가에 비해 달리아스파, 여리한다이어트가 직무만족이 높게 나타났다. 근무 지역에 따라서는 충청도 지역이, 직위에서는 원장이, 근무경력에서는 1년 미만이나 5년 이상이 상대적으로 직무만족이 높은 것으로 나타났다. 이것은 내부마케팅 요인 인식이 높을수록 직무만족이 높다는 것을 알 수 있다. 이 외에 연령, 학력, 입사 전 전공, 거주형태에 따라서는 유의미한 차이가 나타나지 않았다(p>.05). 피부관리실의 전반적인 직무만족은 평균 3.75점으로, 이기영(2015)의 연구에서 서울·경기지역 프랜차이즈 미용실 대상으로 조사한 내부마케팅 요인에 의한 직무만족 평균 3.50점보다 높게 나타났다.
4. 상관관계 분석
피부관리실 내부마케팅 요인과 직원의 직무만족의 상관관계를 알아보기 위해 상관관계 분석을 실시한 결과는 <Table 8>과 같다. 분석결과 피부관리실 내부마케팅 요인의 하위요인별 복리후생(r=.749, p<.001), 커뮤니케이션(r=.680, p<.001), 경영진지원(r=.753, p<.001), 교육훈련(r=.718, p<.001), 권한위임(r=.715, p<.001), 보상제도(r=.810, p<.001)는 직원의 직무만족과 통계적으로 유의미한 정(+)의 상관관계가 있는 것으로 나타났다.
5. 피부관리실 내부마케팅 요인이 직원의 직무만족에 미치는 영향
피부관리실 내부마케팅 요인이 직원의 직무만족에 미치는 영향을 알아보기 위하여 다중회귀분석을 실시한 결과는<Table 9>와 같다. 분석결과 회귀모형의 설명력은 79.2%이고, 회귀식은 통계적으로 유의미한 것으로 분석되었다(F=290.655, p<.001). 독립변수별로는 피부관리실 내부마케팅 요인의 하위요인별 보상제도(β=.313, p<.001), 경영진 지원(β=.180, p<.001), 복리후생(β=.173, p<.001), 교육훈련(β=.140, p<.001), 권한위임(β=.131, p<.001), 커뮤니케이션(β=.118, p<.001)이 직원의 직무만족에 통계적으로 유의미한 정(+)의 영향을 미치는 것으로 나타났다. 내부마케팅 요인과 직무만족의 상관관계 분석 결과에서는 보상제도 요인이 가장 높게 나타났으며 이것은 미용실 종사자 대상으로 한 선행연구 송연숙(2008)의 서울·경기 지역 조사결과, 김필순(2006)의 대구지역 조사결과와 동일하며 이영아(2019)의 서울지역 조사결과 보상시스템이 요인에서 제외 된것과는 다르게 나타나 업종과 지역에 따라 직무만족 요인이 달라질 수 있음을 알 수 있다.
V. 결 론
본 연구는 피부관리실 내부마케팅이 종사원의 직무만족에 미치는 영향을 알아보기 위해 빛채그룹 소속 3개 브랜드사 약손명가, 달리아 스파, 여리한 다이어트에 근무하는 지역별 피부전문가를 대상으로 조사하였다. 본 연구는 피부미용업체 종사원을 대상으로 내부마케팅 요인과 직무만족 상관관계를 연구한 점에서 의의가 있다. 피부관리실 내부마케팅 요인과 직무만족 상관관계에서 보상제도 요인이 가장 높게 나타났으며 경영진 지원, 복리후생, 교육훈련, 권한위임, 커뮤니케이션 순서로 높게 나타나 내부마케팅 하위요인 모두가 종사원의 직무만족에 중요한 요인임을 알 수 있다. 직원에 대한 보상제도를 개발하고 실천하여 피부관리실 종사원의 직무만족을 높일 수 있도록 내부마케팅 전략을 수립하는 것이 중요하다는 것을 시사하고 있다. 본 연구는 한 개의 그룹 소속 종사자를 대상으로 연구한 한계점이 있으므로 향후 다양한 브랜드의 피부관리실 종사원을 대상으로 비교연구하며 직무만족 뿐만아니라 내부마케팅 요인이 고객지향성과 조직몰입에 미치는 영향 등 확대 연구가 이루어지길 기대한다.
Notes
노형진(2001). 한글 SPSS10.0에 의한 조사방법 및 통계분석, 서울: 형설출판사, p.566.