 |
 |
| J Korean Soc Cosmetol > Volume 29(1); 2023 > Article |
|
Abstract
This study aims to investigate the anti-acne efficacy of the plant extract complex (PEC) consisting of Camellia sinensis L. leaf and Castanea crenata bur extract in vitro. The effect of PEC on anti-acne target including sebum production, Cutibacterium acnes (C. acnes)-induced inflammation, 5-alpha reductase activity and free radical scavenging activity was observed. The level of lipid production was measured through nile red staining in sebocytes to confirm the effectiveness of inhibiting sebum production, and C. acnes cultured medium (C. acnes CM) were treated on HEK293-hTLR2 cells to observe TLR2 activity. In addition, regulation of 5-alpha reductase activity was confirmed using rat liver microsomes, and antioxidant capacity was measured by DPPH assay. As a result, PEC showed the inhibitory effect on sebum production up to 59.02┬▒5.13% at 100 ╬╝g/mL and the C. acnes CM with PEC treated group dramatically inhibited the TLR2 activity as much as the control level. At 100 ╬╝g/mL of the PEC, the activity of 5-alpha reductase enzyme activity was suppressed by about 20% compared to the group treated with rat microsomes, and the radical scavenging capacity was measured at 86.83┬▒10.19. These results suggest that PEC, a complex extract of Camellia sinensis L. leaf and Castanea crenata bur, can be used as natural cosmetic raw materials that can relieve acne through inhibition of excessive sebum production, reduction of 5-alpha reductase activity, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties.
ļģ╣ņ░©ļĪ£ ņØ┤ņÜ®ļÉśļŖö ņ░©ļéśļ¼┤(Camellia sinesis L.)ļŖö ļÅÖļ░▒ļéśļ¼┤ ņåŹņØś ņāüļĪØ Ļ┤Ćļ¬®ņØ┤ļŗż. ļģ╣ņ░©ļŖö ļ░®Ē¢źņĪ▒ ņĢīņĮöņś¼ ĒÖöĒĢ®ļ¼╝ņØĖ ĒÅ┤ļ”¼ĒÄśļåĆņØä ĒĢ©ņ£ĀĒĢśĻ│Ā ņ׳ņ£╝ļ®░ ļīĆĒæ£ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ╣┤ĒģīĒé©, ĒöīļØ╝ļ│┤ļģĖņØ┤ļō£, ĒöīļØ╝ļ│┤ļåĆņØ┤ ņ׳ļŗż. ĒÅ┤ļ”¼ĒÄśļåĆņØĆ Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņāØņä▒ņØä ņ¢ĄņĀ£ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ņ£╝ļ®░(Saric et al., 2016), C. acnesņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ┤ ĒÖ£ņä▒ĒÖöļÉ£ ņŚ╝ņ”Øļ░śņØæņØä Ļ░Éņåīņŗ£ĒéżĻ│Ā, ĒĢŁņé░ĒÖöņĀ£ļĪ£ļÅä ņé¼ņÜ®ļÉ£ļŗż(Yoon et al., 2013; Forester & Lambert, 2011).
ļ░żļéśļ¼┤(Castanea crenata Siebold & Zucc, C. crenata)ļŖö ņ░Ėļéśļ¼┤Ļ│╝ņØś ļéÖņŚĮ ĒÖ£ņŚĮ ĻĄÉļ¬®ņ£╝ļĪ£ņŹ© ĒĢ£ļ░śļÅä ņĀäņŚŁņŚÉ ļČäĒżĒĢ£ļŗż. ļ░żļéśļ¼┤ņØś ļŗżņ¢æĒĢ£ ļČĆņ£äļĪ£ļČĆĒä░ ņ¢╗ņ¢┤ņ¦ä ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØĆ ĒĢŁņé░ĒÖö, ĒĢŁĻĘĀ, ĒĢŁņĢīļĀłļź┤ĻĖ░, ņ¦Ćļ░® ņāØņä▒ņ¢ĄņĀ£ ļō▒ņØś ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļéśĒāĆļé┤ļ®░, ļ░żņåĪņØ┤(C. crenata bur)ļŖö ņ┤ØĒżļØ╝Ļ│Ā ĒĢ┤ņä£ ļ░ż ņłśĒÖĢ Ēøä ļ▓äļĀżņ¦ĆļŖö ļČĆņé░ļ¼╝ļĪ£ ļÅÖņØśļ│┤Ļ░ÉņŚÉņä£ļŖö ļŗ©ļÅģ(erysipelas)ņØś ĒĢ£ņĢĮņ×¼ļĪ£ ņé¼ņÜ®ļÉśņŚłļŗżļŖö ĻĖ░ļĪØņØ┤ ņ׳ļŗż(Ahn et al., 2013; Kim et al., 2014; Youn et al., 2016). ļśÉĒĢ£ ļ░żņåĪņØ┤ ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØĆ ĒĢŁņé░ĒÖö, ĒĢŁņŚ╝, Ēŗ░ļĪ£ņŗ£ļéśņĢäņĀ£ ņĀĆĒĢ┤ņÖĆ ņĮ£ļØ╝ņĀ£ļäżņØ┤ņ”ł ņĀĆĒĢ┤ ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļ│┤ņØĖļŗżļŖö Ļ▓░Ļ│╝Ļ░Ć ņ׳ļŗż(Lee et al., 2017).
Ēö╝ļČĆļŖö ņŗĀņ▓┤ņØś Ļ░Ćņן ļ░öĻ╣źņ¬ĮņŚÉ ņ£äņ╣śĒĢ£ ĻĖ░Ļ┤Ćņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ¦łĒÖśņØ┤ ļ░£ņāØĒĢśļ®┤ ļ»ĖņĀü, ņŗ¼ļ”¼ņĀü ņŖżĒŖĖļĀłņŖżĻ░Ć ļÅÖļ░śļÉ£ļŗż. ļīĆĒæ£ņĀü Ēö╝ļČĆņ¦łĒÖś ņżæ ĒĢśļéśņØĖ ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”äņØĆ Ēö╝ņ¦ĆņāśņØ┤ ļ░£ļŗ¼ĒĢ£ ņ¢╝ĻĄ┤, ņØ┤ļ¦ł, Ļ░ĆņŖ┤, ņ¢┤Ļ╣©ļéś ļō▒ ņ£äņ¬ĮņŚÉ ĒØöĒ׳ ļ░£ņāØĒĢśļŖö ļ¦īņä▒ ņŚ╝ņ”Øņä▒ ņ¦łĒÖśņ£╝ļĪ£ 10ļīĆņŚÉ ļé©ņä▒ ĒśĖļź┤ļ¬¼ņØĖ ņĢłļō£ļĪ£ņĀĀ ĒśĖļź┤ļ¬¼ ļČäļ╣äĻ░Ć ņÖĢņä▒ĒĢ┤ņ¦Ćļ®┤ņä£ Ēö╝ņ¦ĆņäĀņØś ĻĖēĻ▓®ĒĢ£ ļ░£ļŗ¼Ļ│╝ ĒĢ©Ļ╗ś ņĮöņÖĆ ņØ┤ļ¦łņŚÉ ņŻ╝ļĪ£ ļ░£ņāØĒĢśļŖö ņé¼ņČśĻĖ░ ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”äĻ│╝ 25ņäĖ ņØ┤ņāüņŚÉņä£ ļéśĒāĆļéśļŖö ņä▒ņØĖ ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”äņ£╝ļĪ£ ļéśļłäņ¢┤ņ¦äļŗż(Williams et al., 2012). ņä▒ņØĖ ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”äņØś ņÜöņØĖņ£╝ļĪ£ļŖö ņŖżĒŖĖļĀłņŖż ĒśĖļź┤ļ¬¼ņØĖ ņĮöļź┤Ēŗ░ņåö, ĒÖöņן, ļ®┤ļÅä, ņŗØņŖĄĻ┤Ć, ļ»ĖņäĖļ©╝ņ¦Ć ļō▒ņØ┤ ņĢīļĀżņĀĖ ņ׳ļŗż(Cong et al., 2019). ņ¦ĆņåŹņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ”ØĻ░ĆĒĢśļŖö ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”ä ĒÖśņ×ÉļōżņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļŗżņ¢æĒĢ£ ņ╣śļŻī ļ░®ļ▓ĢļōżņØ┤ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļÉśņ¢┤ ņÖöņ£╝ļ®░, ļīĆĒæ£ņĀüņØĖ ņ╣śļŻī ĻĖ░ņĀäņ£╝ļĪ£ Ēö╝ņ¦ĆņØś ņØ┤ņāü ļČäļ╣ä ņĪ░ņĀł, ņŚ╝ņ”Øļ░śņØæ ņ¢ĄņĀ£, ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”äĻĘĀņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØ╝ņ╗¼ņ¢┤ņ¦ĆļŖö ĒüÉĒŗ░ļ░ĢĒģīļ”¼ņøĆ ņĢäĒü¼ļäżņŖż(Cutibacterium acnes, C. acnes)ņØś ņ×æņÜ® ņĀĆĒĢ┤, ĒśĖļź┤ļ¬¼ ĻĖ░ņĀä ņĪ░ņĀł, Ļ│╝Ļ░üņ¦łĒÖö ņ¢ĄņĀ£Ļ░Ć ņ׳ļŗż(Kurokawa et al., 2009).
Ēö╝ņ¦Ćļź╝ ļČäļ╣äĒĢśļŖö Ēö╝ņ¦ĆņäĀņØĆ ļ¬©ļéŁ ĒśæļČĆņÖĆ ņŚ░Ļ▓░ļÉśņ¢┤ ļ¬©ļéŁĻ│╝ ĒĢ©Ļ╗ś ĒäĖĒö╝ņ¦Ćņāśļŗ©ņ£äļĪ£ ņĀĢņØśļÉśļ®░ ņ¢╝ĻĄ┤ ņ¬ĮņŚÉ ļåÆņØĆ ļ░ĆļÅäļĪ£ ņĪ┤ņ×¼ĒĢ£ļŗż. Ēö╝ņ¦ĆņäĀņØś ļ░öĻ╣źņĖĄņØĆ peripheral zoneņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĀäĒö╝ņ¦ĆņäĖĒżĻ░Ć ņ”ØņŗØņØä ņŗ£ņ×æĒĢśļ®░ ņĢłņ¬ĮņØś maturation zoneņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØ┤ļÅÖĒĢśļ®┤ņä£ ļČäĒÖöĒĢśņŚ¼ ņ¦Ćļ░® ņåīļ”ĮņØä ĒĢ©ņ£ĀĒĢśĻ▓ī ļÉ£ļŗż. ņĄ£ņóģņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ░Ćņן ņĢłņ¬ĮņŚÉ ņ£äņ╣śĒĢ£ necrotic zoneņŚÉņä£ Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņäĖĒżņØś ļ¦ēĻ│╝ ĒĢĄņØ┤ ļČäĒĢ┤ļÉśļ®┤ņä£ Ēö╝ņ¦Ćļź╝ ļČäļ╣äĒĢśĻ▓ī ļÉ£ļŗż(Clayton et al., 2019). Ēö╝ņ¦ĆļČäļ╣äņØś ņĀĢĒÖĢĒĢ£ ĻĖ░ņĀäņØĆ ņĢäņ¦ü ņĢīļĀżņ¦Ćņ¦Ć ņĢŖņĢśņ£╝ļéś ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņŻ╝ļŖö ņÜöņØĖņ£╝ļĪ£ ņä▒ĒśĖļź┤ļ¬¼ņØĖ ņĢłļō£ļĪ£ņĀĀĻ│╝ ļĀłĒŗ░ļģĖņØ┤ļō£, ņ¦Ćņ¦ł ĒĢ®ņä▒Ļ│╝ Ļ┤ĆļĀ©ļÉ£ ĒÄśļź┤ņśźņŗ£ņóĆ ņ”ØņŗØņ×É ĒÖ£ņä▒ĒÖö ņłśņÜ®ņ▓┤ Ļ░Éļ¦ł(peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, PPAR╬│)ļéś ņŖżĒģīļĪż ņĪ░ņĀł ņÜöņåī Ļ▓░ĒĢ® ļŗ©ļ░▒ņ¦ł-1(sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1, SREBP-1)ņØ┤ ņ¢ĖĻĖēļÉ£ļŗż. ĻĘĖ ņżæņŚÉņä£ļÅä ņĢłļō£ļĪ£ņĀĀņØś ņĪ░ņĀłĻ│╝ Ļ┤ĆļĀ©ĒĢ£ Ēö╝ņ¦ĆļČäļ╣äļŖö in vitroņŚÉņä£ ļģ╝ņ¤üņØ┤ ņ׳ņ¦Ćļ¦ī, ņĢłļō£ļĪ£ņĀĀņØĖ ĒģīņŖżĒåĀņŖżĒģīļĪĀĻ│╝ 5ņĢīĒīī ĒÖśņøÉ ĒÜ©ņåīņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ┤ ņĀäĒÖśļÉśņ¢┤ ĒģīņŖżĒåĀņŖżĒģīļĪĀ ļ│┤ļŗż ļŹö ļåÆņØĆ ĒÖ£ņä▒ņØä ļ│┤ņØ┤ļŖö ļööĒĢśņØ┤ļō£ļĪ£ĒģīņŖżĒåĀņŖżĒģīļĪĀ(dihydrotestosterone, DHT)ņØ┤ Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņäĖĒżņØś ņ”ØņŗØĻ│╝ ņ¦Ćņ¦ł ĒĢ®ņä▒ņØä ņ£ĀļÅäĒĢĀ Ļ▓āņØ┤ļØ╝ļŖö ļģ╝ļ¼ĖļōżĻ│╝, ĒśĖļź┤ļ¬¼ņ╣śļŻīĻ░Ć ņ×äņāüņŚÉņä£ ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļ│┤ņØĖļŗżļŖö Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļōżņØä ļ░öĒāĢņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĢłļō£ļĪ£ņĀĀĻ│╝ Ļ┤ĆļĀ©ļÉ£ ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”ä ņ╣śļŻīļŖö ĻŠĖņżĆĒ׳ ņ¦äĒ¢ēļÉśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż(Barrault et al., 2015; Hazarika, 2021; Sanchez & Keri, 2022).
ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”äņØś ņŻ╝ņÜö ņøÉņØĖĻĘĀņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØ╝ņ╗¼ņ¢┤ņ¦ĆļŖö C. acnesļŖö ļÅģņä▒ņØĖņ×ÉļōżņØä ļČäļ╣äĒĢśņŚ¼ ņŚ╝ņ”Øļ░śņØæņØä ņØ╝ņ£╝Ēé©ļŗż. Ēü¼ļ”¼ņŖżĒŗ░-ņĢ│Ēé©ņŖż-ļ©╝ņ╣ś-Ēö╝Ēä░ņŖ©(Christie-Atkins-Munch-Peterson, CAMP)ņØĖņ×É, ļ”¼ĒīīņĢäņĀ£, ņŗ£ņĢīļ”¼ļŗżņĢäņĀ£ ļō▒ņØś ļÅģņä▒ņØĖņ×ÉļōżņØĆ Toll-ņ£Āņé¼ ņłśņÜ®ņ▓┤2(Toll-like receptor 2, TLR2)ņŚÉ ņ×æņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ĒĢĄņØĖņ×É ņ╣┤Ēīīļ╣ä(Nuclear factor-╬║B, NF-╬║B)ļź╝ ĒÖ£ņä▒ĒÖöņŗ£ņ╝£ņä£ Ļ░üņ¦łĒśĢņä▒ņäĖĒż, Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņäĖĒż, ĻĘĖļ”¼Ļ│Ā ļ®┤ņŚŁņäĖĒżļĪ£ļČĆĒä░ ņĀä ņŚ╝ņ”Øņä▒ ņé¼ņØ┤ĒåĀņ╣┤ņØĖņØä ļČäļ╣äĒĢśĻ▓ī ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņŚ╝ņ”Ø ļ░śņØæņØä ņØ╝ņ£╝ĒéżļŖöļŹ░, ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ņŚ░ņåŹņĀüņØĖ ņ×æņÜ®ļōżņØĆ C. acnesņØś ņ¦æļØĮ ĒśĢņä▒ņØä ņ£ĀļÅäĒĢśļ®░ ņĄ£ņóģņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ļŖö ņāØņ▓┤ļ¦ēņØä ĒśĢņä▒ĒĢśĻ│Ā ĒĢŁņāØņĀ£ ņĀĆĒĢŁņä▒ņØä ļéśĒāĆļé┤ ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”ä ņ╣śļŻīņŚÉ ņ¢┤ļĀżņøĆņØä ļŹöĒĢśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż(Burkhart & Burkhart, 2003; Zhang et al., 2019).
ĒśĖņżæĻĄ¼ņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØĆ ņŗØņäĖĒżļŖö ņ╣©ņ×ģĒĢśļŖö ļ»ĖņāØļ¼╝ņØä ņÜ®ĒĢ┤ĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ĒÖ£ņä▒ņé░ņåīņóģ(reactive oxygen species, ROS)ņØä ņāØņä▒ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī, Ļ│╝ļÅäĒĢ£ ROSņØś ņāØņé░ņØĆ ņŻ╝ļ│Ć ņĪ░ņ¦üņŚÉ ņåÉņāüņØä ņ£Āļ░£ĒĢ£ļŗż. ĒŖ╣Ē׳ļéś ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”äņØś ņŚ╝ņ”Ø ļ░śņØæņØ┤ ņØ╝ņ¢┤ļéśļŖö Ļ││ņŚÉņä£ļŖö C. acnesņØś ņ×ÉĻĘ╣ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņŗØņäĖĒżļĪ£ļČĆĒä░ņØś ROS ņāØņä▒ņØ┤ ļŹöņÜ▒ ņ”ØĻ░ĆĒĢśņŚ¼ ņäĖĒżņŚÉ ņŗ¼ĒĢ£ ņåÉņāüņØä ņØ╝ņ£╝ĒéżĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ ROSņØś ņāØņä▒ņØä ņ¢ĄņĀ£ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”ä ņ╣śļŻīņŚÉ ņżæņÜöĒĢśļŗż(Akamatsu & Horio, 1998).
ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļŖö ĒĢŁ ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”ä ĒÜ©ļŖźĒāĆĻ▓¤ ņäĀĒ¢ē ņŖżĒü¼ļ”¼ļŗØ ņŗ£ĒŚśņŚÉņä£ ļģ╣ņ░©ņÖĆ ļ░żņåĪņØ┤ ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØä ņäĀļ│äĒĢśņśĆņ£╝ļ®░, ņØ┤ļōż ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØä ļÅÖļ¤ē ļ╣äņ£©ļĪ£ Ēś╝ĒĢ®ĒĢ£ ņŗØļ¼╝ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝(plant extract complex, PEC)ņØä ņĀ£ņĪ░ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņØ┤Ēøä ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØś ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”ä ņÖäĒÖö ĻĖ░ļŖźņØä ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢśņŚ¼ Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņāØņä▒ ņ¢ĄņĀ£ļŖź, 5 ņĢīĒīī ĒÖśņøÉĒÜ©ņåī ĒÖ£ņä▒ ņ¢ĄņĀ£ļŖź, ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”äĻĘĀņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ£ ņŚ╝ņ”Ø ņÖäĒÖö ĒÜ©ļŖź ļ░Å ĒĢŁņé░ĒÖö ĒÜ©ļŖźņØä in vitro ņłśņżĆņŚÉņä£ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņäĖĒżņØś ļČäĒÖöļź╝ ņ£ĀļÅäĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ņé¼ņÜ®ļÉ£ Ēīöļ»ĖĒŖĖņé░Ļ│╝ Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņŚ╝ņāēņŚÉ ņé¼ņÜ®ļÉ£ ļéśņØ╝ ļĀłļō£ļŖö Sigma-Aldrich(St. Louis, MO, USA)ņŚÉņä£ ĻĄ¼ņ×ģĒĢśņŚ¼ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. 5 ņĢīĒīī ĒÖśņøÉĒÜ©ņåī ņ¢ĄņĀ£ļŖź ņŗ£ĒŚśņŚÉ ņé¼ņÜ®ļÉ£ dithiothreitolļŖö Thermo Fisher Scientific(Waltham, MA, USA)ņŚÉņä£, NADPHļŖö Roche Holding AG(Basel, Switzerland)ņŚÉņä£ ĻĄ¼ļ¦żĒĢśņśĆņ£╝ļ®░, testosteroneņØĆ ChemFaces (Hubei, China)ņŚÉņä£, potassium phosphateņÖĆ rat liver microsomeņØĆ Sigma-AldrichņŚÉņä£ Ļ░üĻ░ü ĻĄ¼ļ¦żĒĢśņŚ¼ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņäĖĒżņāØņĪ┤ņä▒ ņĖĪņĀĢņØä ņ£äĒĢ£ 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazoyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide(MTT)ņÖĆ DPPH assayņŚÉ ņé¼ņÜ®ļÉ£ 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl(DPPH), ņĢäņŖżņĮöļź┤ļĖīņé░ņØĆ Sigma-AldrichņŚÉņä£ ĻĄ¼ļ¦żĒĢśņŚ¼ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ļ░żļéśļ¼┤ ņ┤ØĒżļŖö ĒÆŹņ▓£ņØĖņé╝ņĢĮņ┤łņśüļåŹņĪ░ĒĢ®(Chungcheongnam-do, Korea)ņŚÉņä£ ĻĄ¼ņ×ģĒĢśņśĆņ£╝ļ®░, ļģ╣ņ░© ņ×ÄņØĆ ņś¼Ēŗ░ņŖż ņśüļåŹņĪ░ĒĢ®ļ▓ĢņØĖ(Jeju, Korea)ņŚÉņä£ ĻĄ¼ņ×ģĒĢśņŚ¼ ņŗżĒŚśņŚÉ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ļÉ£ ļ░żļéśļ¼┤ ņ┤ØĒżņŚÉ ļ¼╝ņØä ņ▓©Ļ░ĆĒĢ£ Ēøä 90oCņŚÉņä£ 3 h ļÅÖņĢł Ļ░ĆņŚ┤ ņČöņČ£ĒĢśĻ│Ā, Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ļÉ£ ļģ╣ņ░© ņ×ÄņŚÉ ļ¼╝ņØä ņ▓©Ļ░ĆĒĢ£ Ēøä 80oCņŚÉņä£ 3 h ļÅÖņĢł Ļ░ĆņŚ┤ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņČöņČ£ĒĢ£ļŗż. Ļ░üĻ░üņØś ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØä Ļ░ÉņĢĢ ļåŹņČĢĻĖ░(Rotary evaporator N-1000, EYELA, Japan)ļź╝ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ļåŹņČĢĒĢ£ ļŗżņØī ļČäļ¼┤ Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ĻĖ░(TF-S2L Mini Spray Dryer, Tefic Biotech Co., Limited, China)ļź╝ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ Ļ░üĻ░ü ļČäļ¦ÉĒÖöĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ļ░żņåĪņØ┤:ļģ╣ņ░© ļ╣äņ£©ņØä 1:1 ļÅÖļ¤ē ļ╣äņ£©ļĪ£ Ēś╝ĒĢ®ĒĢ£ ņŗ£ļŻīļź╝ ĒÜ©ļŖźĒÅēĻ░ĆņŚÉ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
ņØĖĻ░ä Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņäĖĒż(Celprogen, Torrance, CA, USA)ļŖö Sebocyte Complete Growth Media (Celprogen)ņŚÉņä£ 37oC, 5% CO2 ņĪ░Ļ▒┤ņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ░░ņ¢æĒĢ£ ļÆż ņŗżĒŚśņŚÉ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. 100 ╬╝M Ēīöļ»ĖĒŖĖņé░ņØä ņ▓śļ”¼ĒĢśņŚ¼ Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņāØņä▒ņØä ņ£ĀļÅäĒĢśņśĆņ£╝ļ®░, Ēīöļ»ĖĒŖĖņé░Ļ│╝ ĒĢ©Ļ╗ś ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØä 1, 10, 50, 100 ╬╝g/mLļĪ£ ĒؼņäØĒĢśņŚ¼ ņ▓śļ”¼ĒĢ£ ļÆż, 72 h ļÅÖņĢł ļ░░ņ¢æĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ļ░░ņ¢æĒĢ£ ņäĖĒżļź╝ 4% Ēżļ”äņĢīļŹ░ĒĢśņØ┤ļō£ļĪ£ 10ļČäĻ░ä Ļ│ĀņĀĢĒĢśĻ│Ā 10 ╬╝g/mL ļéśņØ╝ ļĀłļō£ļź╝ 1:100ņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒؼņäØĒĢśņŚ¼ 15ļČäĻ░ä ņŚ╝ņāēĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ĒĢĄņØĆ Hoechst 33342ļĪ£ ņŚ╝ņāēĒĢśņśĆņ£╝ļ®░ ĒśĢĻ┤æĒśäļ»ĖĻ▓Į(EVOS┬«FL, Thermo Fisher Scientific)ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢśņśĆļŗż. Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņāØņä▒ ņĀĢļÅäļź╝ ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ£ ņé¼ņ¦ä ļČäņäØņØĆ ImageJļź╝ ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
C. acnes ĻĘĀņØĆ ATCC(American Type Culture Collection ATCC, Manassas, VA, USA)ņŚÉņä£ ĻĄ¼ļ¦żĒĢśņśĆņ£╝ļ®░, Reinforced Clostridial Medium(RCM, Difco, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA)ņŚÉņä£ 37oC ĒśÉĻĖ░ņä▒ ņĪ░Ļ▒┤ņ£╝ļĪ£ 48 h ļ░░ņ¢æĒĢ£ ļÆż ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. C. acnesļŖö 1 ├Ś 107 ņĮ£ļĪ£ļŗł ĒśĢņä▒ ļŗ©ņ£ä(colony forming units, CFU)/mLļĪ£ ņĪ░ņĀĢĒĢśņśĆņ£╝ļ®░ 96ņø░ ĒöīļĀłņØ┤ĒŖĖ Ļ░ü ņø░ ļ¦łļŗż 1 ├Ś 105 CFU/mLļĪ£ ņäĖĻĘĀ ĒśäĒāüņĢĪņØä ņĀæņóģĒĢśĻ│Ā 500, 1000, 2000 ╬╝g/mLļĪ£ ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØä ņ▓śļ”¼ĒĢ£ ņĪ░Ļ▒┤(PEC-treated C. acnes cultured media; C. acnes ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝)Ļ│╝ ņ▓śļ”¼ĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņØĆ ņĪ░Ļ▒┤(C. acnes cultured media; C. acnes CM)ņ£╝ļĪ£ 18 h ļÅÖņĢł ļ░░ņ¢æĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ļ░░ņ¢æņĢĪņØĆ ļ¬©ņĢäņä£ 0.22 ļ¦łņØ┤Ēü¼ļĪĀ ĻĖ░Ļ│Ą Ēü¼ĻĖ░ņØś ĒĢäĒä░(EMD Millipore, Temecula, CA, USA)ļĪ£ ņŚ¼Ļ│╝ĒĢ£ Ēøä ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
TLR2 ĒÖ£ņä▒ņØä ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢśņŚ¼ human TLR2/NF-╬║B/SEAP reporter HEK293 ņäĖĒż(HEK293-BlueTM hTLR2, InvivoGen, SanDiego, CA, USA)ļź╝ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. HEK293-hTLR2 ņäĖĒżļź╝ 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Gibco, Carlsbad, CA, USA)ņØ┤ ĒżĒĢ©ļÉ£ DulbeccoŌĆÖs modified EagleŌĆÖs medium (DMEM, Hyclone, Logan, UT, USA) ņŚÉņä£ 37oC, 5% CO2 ņĪ░Ļ▒┤ņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ░░ņ¢æĒĢ£ ļÆż ņŗżĒŚśņŚÉ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. HEK293-hTLR2 ņäĖĒżņŚÉ C. acnes CMĻ│╝ C. acnes ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØä 1/100ļĪ£ ņ▓śļ”¼ĒĢśņŚ¼ 6 h ļÅÖņĢł ļ░░ņ¢æĒĢ£ ļÆż, ļ░░ņ¢æņĢĪņØä QUANTI-BlueTM ņÜ®ņĢĪ(InvivoGen)Ļ│╝ 30ļČä ļÅÖņĢł ļ░śņØæņŗ£ņ╝£ secreted alkaline phosphatase(SEAP) ĒÖ£ņä▒ņØä 620 nm ĒīīņןņŚÉņä£ ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢśņśĆļŗż(Epoch, Bio-Tek Inc., Winooski, VT, USA).
HEK293-hTLR2ņØś ņäĖĒżņāØņĪ┤ņä▒ņØä ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢśņŚ¼ HEK293-hTLR2 ņäĖĒżļź╝ 10% fetal bovine serum(FBS, Gibco)ņØ┤ ĒżĒĢ©ļÉ£ DMEMņŚÉņä£ 37oC, 5% CO2 ņĪ░Ļ▒┤ņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ░░ņ¢æĒĢ£ ļÆż ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØä 1, 10, 50, 100 ╬╝g/mLļĪ£ ņ▓śļ”¼ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. 6 h ļÅÖņĢł ļ░░ņ¢æĒĢ£ ļÆż, 0.1 mg/mL MTT ņÜ®ņĢĪ(Sigma-Aldrich)ņØä 1 h ļÅÖņĢł ņ▓śļ”¼ĒĢśĻ│Ā DMSOņŚÉ formazanņØä ļģ╣ņŚ¼ 570 nm ĒīīņןņŚÉņä£ ņäĖĒżņāØņĪ┤ņä▒ņØä ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢśņśĆļŗż(Epoch, Bio-Tek Inc.).
1mmol/L dithiothreitol, pH 6.5, 40 mmol/L potassium phosphate, 100 ╬╝mol/L NADPHņÖĆ 3.5 ╬╝mol/L testosteroneņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ░śņØæņÜ®ņĢĪņØä ņĀ£ņĪ░ĒĢśņŚ¼ 20ļČä ļÅÖņĢł ņāüņś©ņŚÉ ļåōņĢäļæÉņŚłļŗż. ļ░śņØæņÜ®ņĢĪņŚÉ 20 ╬╝g/mL ļלĒŖĖ Ļ░ä ļ¦łņØ┤Ēü¼ļĪ£ņóĆ(Rat liver microsome)Ļ│╝ Ēö╝ļéśņŖżĒģīļØ╝ņØ┤ļō£, ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØä ņ▓©Ļ░ĆĒĢśĻ│Ā 37oCņŚÉņä£ 1 h ļÅÖņĢł ļ░śņØæņŗ£ņ╝░ļŗż. ļ░śņØæņÜ®ņĢĪņØä ļÅÖĻ▓░ Ļ▒┤ņĪ░ĒĢ£ Ēøä ļ®öĒāäņś¼ņŚÉ ļģ╣ņŚ¼ 0.2 ļ¦łņØ┤Ēü¼ļĪĀ ĒĢäĒä░(Pall, NY, USA)ļĪ£ ņŚ¼Ļ│╝ĒĢśĻ│Ā HPLC(Waters 2695 Separation Module, Waters 2996 Photodiode Array Detector, Waters, MA, USA)ļĪ£ ĒģīņŖżĒåĀņŖżĒģīļĪĀ ņ¢æņØä ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņØ┤ļÅÖņāüņØĖ 0.1% ĒŖĖļ”¼ĒöīļŻ©ņśżļĪ£ ņĢäņäĖĒŖĖņé░:ņĢäņäĖĒåĀļŗłĒŖĖļ”┤(50:50,v/v)ņØś ņ£ĀņåŹņØä 1.0 mL/min ĻĖ░ļ░śņ£╝ļĪ£ ļČäņäØĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØä 1 , 10, 50, 100 ╬╝ g /mLņØś ļåŹļÅäļĪ£ 100% ļ®öĒāäņś¼ņŚÉ ĒؼņäØĒĢśņŚ¼ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. DPPHļŖö 2 mM ļåŹļÅäļĪ£ ņĀ£ņĪ░ĒĢ£ ļÆż, 100% ļ®öĒāäņś¼ņŚÉ ĒؼņäØĒĢśņŚ¼ 517 nmņŚÉņä£ ĒØĪĻ┤æļÅäļź╝ 0.5 ĻĖ░ņżĆņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ¦×ņČś Ēøä, ņŗżĒŚśņŚÉ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśņśĆļŗż. DPPHņÖĆ ĒؼņäØĒĢ£ ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØä 1:1ļĪ£ Ēś╝ĒĢ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņāüņś©ņŚÉņä£ 30ļČäĻ░ä ļ░śņØæņŗ£Ēé© ļÆż, 517 nmņŚÉņä£ ļé©ņĢäņ׳ļŖö DPPHņØś ņ¢æņØä ĒØĪĻ┤æļÅäļĪ£ ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢśņśĆļŗż(Epoch, Bio-Tek Inc.). ļīĆņĪ░ĻĄ¼ļĪ£ļŖö ļÅÖļ¤ēņØś ļ®öĒāäņś¼ņØä ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśņśĆņ£╝ļ®░, ņŗ£ļŻīņØś ĒĢŁņé░ĒÖöļŖźņØĆ ļīĆņĪ░ĻĄ¼ņÖĆ ļ╣äĻĄÉĒĢśņŚ¼ Ļ░ÉņåīļÉ£ ĒØĪĻ┤æļÅä Ļ░ÆņØä ĒŹ╝ņä╝ĒŖĖļĪ£ Ļ│äņé░ĒĢśņŚ¼ ļéśĒāĆļé┤ņŚłļŗż.
Radical Scavenging Activity (%) = (1 - Absorbance of test material/Absorbance of control) ├Ś 100
Ļ│╝ļÅäĒĢ£ Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņāØņä▒ņØĆ ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”äņØś ņŻ╝ņÜö ņøÉņØĖņØ┤ņ×É Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļĪ£ Ļ│╝ļŗżĒĢśĻ▓ī ņāØņä▒ļÉśļŖö Ēö╝ņ¦Ćļź╝ Ļ░Éņåīņŗ£ĒéżļŖö Ļ▓āņØ┤ ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”ä ļ░£ņāØņØä ņżäņØ┤Ļ▒░ļéś ĻĘĖ ļ│æļ│ĆņØä ņÖäĒÖöĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņŚÉ ņ׳ņ¢┤ņä£ ņżæņÜöĒĢśļŗż(Li et al., 2017). ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņāØņä▒Ļ│╝ ĻĘĖ ņ¢ĄņĀ£ļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ņØĖĻ░ä Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņäĖĒżņŚÉ Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņāØņä▒ ņ£ĀļÅä ļ¼╝ņ¦łņØĖ Ēīöļ»ĖĒŖĖņé░Ļ│╝, ļģ╣ņ░©-ļ░żņåĪņØ┤ņØś ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØä ņ▓śļ”¼ĒĢśņŚ¼ Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņäĖĒż ļé┤, ņāØņä▒ļÉśļŖö Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņĀĢļÅäļź╝ ļéśņØ╝ ļĀłļō£ ņŚ╝ņāēņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ĒżĒÖöņ¦Ćļ░®ņé░ņØĖ Ēīöļ»ĖĒŖĖņé░ņØĆ Ēö╝ļČĆņØś ņ¦Ćņ¦ł ĒĢ©ļ¤ē ņĪ░ņĀł ļ░Å ņŚ╝ņ”Ø ļ░śņØæņŚÉ Ļ┤ĆņŚ¼ĒĢĀ ļ┐É ņĢäļŗłļØ╝, Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņäĖĒżņØś ņ¦Ćņ¦ł ĒĢ©ļ¤ēĻ│╝ ņżæņä▒ņ¦Ćļ░® ņłśņ╣śļź╝ ņ”ØĻ░Ćņŗ£Ēé¼ ņłś ņ׳ļŗżĻ│Ā ņĢīļĀżņĀĖ ņ׳ļŗż(Choi et al., 2019).
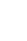
ļģ╣ņ░©-ļ░żņåĪņØ┤ņØś ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØś Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņāØņä▒ ņ¢ĄņĀ£ļŖźņØä ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ Fig. 1Ļ│╝ Ļ░Öļŗż. Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņäĖĒż ļé┤ņŚÉņä£ Ēīöļ»ĖĒŖĖņé░ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ĀļÅäļÉ£ Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņāØņä▒ņØĆ ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ ņ▓śļ”¼ ņŗ£, ļåŹļÅä ņØśņĪ┤ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ░ÉņåīĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļ│┤ņśĆļŗż. Ēīöļ»ĖĒŖĖņé░Ļ│╝ ļ╣äĻĄÉĒĢśņśĆņØä ļĢī, ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ ņ▓śļ”¼ ņŗ£ 1 ╬╝g/mLņŚÉņä£ 14.74┬▒2.32%, 10 ╬╝g/mLņŚÉņä£ 34.79┬▒7.34%, 50 ╬╝g/mL ņŚÉņä£ 51.25┬▒6.46%, 100 ╬╝g/mLņŚÉņä£ 59.02┬▒5.13%ņØś Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņāØņä▒ņ¢ĄņĀ£ļŖźņØä ļ│┤ņśĆļŗż. ņØ┤ļŖö ļģ╣ņ░©ņŚÉ ĒżĒĢ©ļÉ£ ņŻ╝ņÜö ĒÅ┤ļ”¼ĒÄśļåĆņØĖ Epigallocatechin-3-gallate(EGCG)ņÖĆ ļīĆĒæ£ņĀüņØĖ ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”ä ņ╣śļŻīņĀ£ņØĖ isotretinoin(13-cis-RA)ņØ┤ Ļ░üĻ░ü 100 ╬╝MĻ│╝ 1 ╬╝MņŚÉņä£ 40% ņĀĢļÅäņØś Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņ¢ĄņĀ£ļŖźņØä ļ│┤ņØ┤Ļ│Ā Ļ▓Įņ”Ø ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”ä ņ╣śļŻīņŚÉ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢśļŖö adapaleneņØ┤ 10 nMņŚÉņä£ 55% ņĀĢļÅäņØś Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņ¢ĄņĀ£ļŖźņØä ļ│┤ņØ┤ļŖö Ļ▓āĻ│╝ ļ╣äņŖĘĒĢ£ ņłśņżĆņ£╝ļĪ£ ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŗż(Im et al., 2012; Sato et al., 2013).
ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”äņØĆ ļ¦īņä▒ ņŚ╝ņ”Øņä▒ ņ¦łĒÖśņ£╝ļĪ£ ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”ä ņ╣śļŻīļź╝ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ņŚ╝ņ”Øļ░śņØæņØä ļé«ņČöļŖö ļ░®ļ▓ĢļōżņØ┤ Ļ│ĀļĀżļÉ£ļŗż. ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ņŚ╝ņ”Øļ░śņØæņØĆ ņŻ╝ļĪ£ C. acnesņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ┤ ņ£ĀļÅäļÉśļŖöļŹ░, Ēö╝ļČĆ ņäĖĒżļéś ļ®┤ņŚŁ ņäĖĒż ļé┤ņŚÉņä£ ņŚ╝ņ”Øļ░śņØæ ņŗĀĒśĖļź╝ ĒÖ£ņä▒ĒÖöņŗ£ņ╝£ ņŚ╝ņ”Øņä▒ ņé¼ņØ┤ĒåĀņ╣┤ņØĖ ļČäļ╣äļź╝ ņ┤ēņ¦äĒĢ£ļŗż. C. acnesļŖö ļ”¼ĒīīņĢäņĀ£, ņŗ£ņĢīļ”¼ļŗżņĢäņĀ£ņÖĆ CAMPņÖĆ Ļ░ÖņØĆ ļŗżņ¢æĒĢ£ ļÅģņä▒ ņØĖņ×ÉļōżņØä ļČäļ╣äĒĢśĻ│Ā, ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ņØĖņ×ÉļōżņØĆ ņäĖĒżļ¦ēņŚÉ ņ£äņ╣śĒĢ£ TLR2ņÖĆ ļ░śņØæĒĢśņŚ¼ ņäĖĒż ļé┤ņŚÉņä£ NF-╬║B ņŗĀĒśĖļź╝ ĒÖ£ņä▒ĒÖöĒĢ£ļŗż. ĒÖ£ņä▒ĒÖöļÉ£ ņŗĀĒśĖļŖö I╬║B ĒéżļéśņĢäņĀ£(I╬║B kinase, IKK)ļź╝ ņØĖņé░ĒÖöņŗ£ĒéżĻ│Ā ņäĖĒżņ¦łņŚÉ ņĪ┤ņ×¼ĒĢśļŖö NF-╬║BļĪ£ļČĆĒä░ I╬║Bļź╝ ļČäļ”¼ņŗ£ņ╝£ NF-╬║BĻ░Ć ĒĢĄļé┤ļĪ£ ņØ┤ļÅÖĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳Ļ▓ī ĒĢ┤ņżīņ£╝ļĪ£ņŹ©, ņŚ╝ņ”Øņä▒ ņé¼ņØ┤ĒåĀņ╣┤ņØĖĻ│╝ Ļ┤ĆļĀ©ļÉ£ ņ£ĀņĀäņ×ÉņØś ļ░£ĒśäņØä ņ£ĀļÅäĒĢ£ļŗż(Kawasaki & Kawai, 2014). ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ĻĖ░ņĀäņØä ļ░öĒāĢņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØĖĻ░ä TLR2 ņ£ĀņĀäņ×Éļź╝ ļ░£ĒśäĒĢśļŖö SEAP reporter 293 ņäĖĒż(HEK293-hTLR2 ņäĖĒż)ļź╝ ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ĒĢŁņŚ╝ ĒÜ©ļŖźņØä ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
ņŗżĒŚśņØä ņ£äĒĢ┤ C. acnesļź╝ ļģ╣ņ░©-ļ░żņåĪņØ┤ņØś ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝Ļ│╝ ĒĢ©Ļ╗ś ļ░░ņ¢æĒĢ£ ļÆż, ļ░░ņ¢æņĢĪņØä ļ¬©ņĢä HEK293-hTLR2 ņäĖĒżņŚÉ ņ▓śļ”¼ĒĢśņŚ¼ ĒĢŁņŚ╝ ĒÜ©ļŖźņØä ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ Fig . 2ņÖĆ Ļ░Öļŗż. ņØ┤ļŖö C. acnesļĪ£ļČĆĒä░ ļČäļ╣äļÉśļŖö ļÅģņä▒ļ¼╝ņ¦łņØä PECĻ░Ć ņ¢ĄņĀ£ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖöņ¦Ć ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ņłśĒ¢ēļÉśņŚłņ£╝ļ®░, ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØĖ PECļź╝ ņ▓śļ”¼ĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖĻ│Ā C. acnesļ¦ī ļ░░ņ¢æĒĢ£ ļ░░ņ¢æņĢĪ(C. acnes CM)Ļ│╝ C. acnesļź╝ PECņÖĆ ĒĢ©Ļ╗ś ļ░░ņ¢æĒĢśņŚ¼ ņ¢╗ņØĆ ļ░░ņ¢æņĢĪ(PEC-treated C. acnes cultured media; C. acnes ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝)ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ¦äĒ¢ēĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ļģ╣ņ░©-ļ░żņåĪņØ┤ ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØś ļŗ©ļÅģ ņ▓śļ”¼ ņŗ£, 100 ╬╝g/mLĻ╣īņ¦Ć ņäĖĒż ļÅģņä▒ņØä ļéśĒāĆļé┤ņ¦Ć ņĢŖņØīņØä ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśņśĆļŗż(Fig. 2A). ļśÉĒĢ£ C. acnes CMĻ│╝ C. acnes ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ ņŚŁņŗ£, ņłśĒ¢ēĒĢ£ ņŗżĒŚś ļåŹļÅä ļé┤ņŚÉņä£ ņäĖĒż ļÅģņä▒ņØ┤ ņŚåņØīņØä ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśņśĆļŗż(Fig. 2B). ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØä ņ▓śļ”¼ĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖĻ│Ā C. acnesļ¦ī ļ░░ņ¢æĒĢ£ ļ░░ņ¢æņĢĪņØä ņ▓śļ”¼ĒĢ£ Ļ▓āņŚÉ ļ╣äĒĢ┤ ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝Ļ│╝ ĒĢ©Ļ╗ś ļ░░ņ¢æĒĢ£ ļ░░ņ¢æņĢĪņØä ņ▓śļ”¼ĒĢ£ ņŗżĒŚśĻĄ░ņŚÉņä£ļŖö TLR2 ĒÖ£ņä▒ņØ┤ ņÜ░ņłśĒĢśĻ▓ī ņ¢ĄņĀ£ļÉśņŚłņØīņØä ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśņśĆļŗż(Fig. 2C). ņØ┤ļŖö ņäĀĒ¢ēņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ ņ¦äĒ¢ēļÉ£ C. acnesņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ĒĢŁĻĘĀ ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ ņŗżĒŚśĻ│╝ C. acnesĻĘĀņØä ņ▓śļ”¼ĒĢśņŚ¼ ĒĢŁņŚ╝ ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢ£ ņŗżĒŚśĻ│╝ļŖö ļŗ¼ļ”¼, C. acnesņØś ņ¦üņĀæņĀüņØĖ ņ×æņÜ®ņØ┤ ņĢäļŗłļŹöļØ╝ļÅä C. acnesļĪ£ ļČĆĒä░ ļČäļ╣äļÉśļŖö ļÅģņä▒ļ¼╝ņ¦łņØ┤ TLR2ļź╝ ĒÖ£ņä▒ĒÖöĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳Ļ│Ā, ļģ╣ņ░©-ļ░żņåĪņØ┤ņØś ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØ┤ C. acnesļĪ£ļČĆĒä░ ļČäļ╣äļÉśļŖö ļÅģņä▒ļ¼╝ņ¦łņØś ņłśņżĆņØä ļé«ņČżņ£╝ļĪ£ņŹ© ņŚ╝ņ”Øļ░śņØæņØä ņ¢ĄņĀ£ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ņØä Ļ▓āņØ┤ļØ╝ļŖö Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļ│┤ņŚ¼ņżĆļŗż.
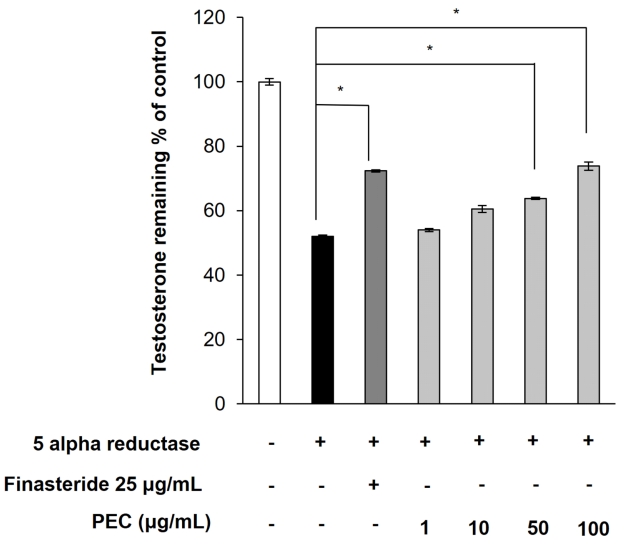
ņĢłļō£ļĪ£ņĀĀņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ£ Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņāØņä▒ņØĆ ĒģīņŖżĒåĀņŖżĒģīļĪĀņØä DHTļĪ£ ņĀäĒÖśĒĢśļŖö 5 ņĢīĒīī ĒÖśņøÉĒÜ©ņåī ĒÖ£ņä▒Ļ│╝ Ļ┤ĆļĀ©ņØ┤ ņ׳ļŗż. DHTļŖö ĒģīņŖżĒåĀņŖżĒģīļĪĀļ│┤ļŗż ņĢłļō£ļĪ£ņĀĀ ņłśņÜ®ņ▓┤ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņ╣£ĒÖöļÅäĻ░Ć ļŹö ļåÆņĢäņä£ Ļ▓░ĒĢ®ņØ┤ ņĢłņĀĢņĀüņØ┤Ļ│Ā ĻĘĖ ĒÜ©Ļ│╝Ļ░Ć ļŹö ļåÆļŗż(Makrantonaki et al., 2011). ļö░ļØ╝ņä£ 5 ņĢīĒīī ĒÖśņøÉĒÜ©ņåīņØś ĒÖ£ņä▒ņØä ņĀĆĒĢ┤ĒĢśņŚ¼ DHTņØś ņāØņä▒ņØä Ļ░Éņåīņŗ£Ēéżļ®┤, ņĢłļō£ļĪ£Ļ▓É ņŗĀĒśĖļź╝ ņĀĆĒĢ┤ĒĢ©ņ£╝ļĪ£ņŹ© Ļ│╝ļÅäĒĢ£ Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņāØņä▒ņØä ņ¢ĄņĀ£ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż(Lai et al., 2012). ņØ┤ļź╝ ĻĖ░ļ░śņ£╝ļĪ£ 5 ņĢīĒīī ĒÖśņøÉĒÜ©ņåī ĒÖ£ņä▒ņ¢ĄņĀ£ ĒÜ©ļŖźņØä ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ 5 ņĢīĒīī ĒÖśņøÉĒÜ©ņåīļź╝ ĒżĒĢ©ĒĢśļŖö ļלĒŖĖĻ░ä ļ¦łņØ┤Ēü¼ļĪ£ņóĆņØä ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØś 5 ņĢīĒīī ĒÖśņøÉĒÜ©ņåī ĒÖ£ņä▒ņ¢ĄņĀ£ ĒÜ©ļŖźņØä ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØä ĒģīņŖżĒåĀņŖżĒģīļĪĀ, ļלĒŖĖ ļ¦łņØ┤Ēü¼ļĪ£ņóĆĻ│╝ ļåŹļÅä ļ│äļĪ£ ļ░śņØæņŗ£Ēé© Ēøä, ļé©ņĢä ņ׳ļŖö ĒģīņŖżĒåĀņŖżĒģīļĪĀņØś ņāüļīĆņĀüņØĖ ņ¢æņ£╝ļĪ£ 5 ņĢīĒīī ĒÖśņøÉĒÜ©ņåīņØś ĒÖ£ņä▒ņØä ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ Fig. 3Ļ│╝ Ļ░ÖņØ┤ ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŗż. Ēö╝ļéśņŖżĒģīļØ╝ņØ┤ļō£ļŖö ņ¢æņä▒ļīĆņĪ░ĻĄ░ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņé¼ņÜ®ļÉśņŚłļŗż. ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØä ņ▓śļ”¼ĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņØĆ ļīĆņĪ░ĻĄ░Ļ│╝ ļ╣äĻĄÉĒĢśņŚ¼ ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØä ņ▓śļ”¼ĒĢ£ ņŗżĒŚśĻĄ░ņØś ņāüļīĆņĀüņØĖ ĒģīņŖżĒåĀņŖżĒģīļĪĀ ņ¢æņØ┤ 1 ╬╝g/mLņŚÉņä£ 54.04┬▒0.47%, 10 ╬╝g/mLņŚÉņä£ 60.53┬▒1.05%, 50 ╬╝g/mLņŚÉņä£ 63.82┬▒0.32%, 100 ╬╝g/mLņŚÉņä£ 73.84┬▒1.29%ļĪ£ ņĖĪņĀĢļÉśņŚłļŗż. ņØ┤ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļŖö ļלĒŖĖ Ļ░ä ļ¦łņØ┤Ēü¼ļĪ£ņóĆ ļé┤ 5 ņĢīĒīī ĒÖśņøÉĒÜ©ņåī ĒÖ£ņä▒ņØ┤ ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ┤ ņ¢ĄņĀ£ļÉśņ¢┤ ĒģīņŖżĒåĀņŖżĒģīļĪĀņØ┤ DHTļĪ£ ņĀäĒÖśļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖĻ│Ā ļé©ņĢäņ׳ņØīņØä ņŗ£ņé¼ĒĢ£ļŗż. ļśÉĒĢ£ ņ¢æņä▒ļīĆņĪ░ĻĄ░ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņō░ņØĖ 5 ņĢīĒīī ĒÖśņøÉĒÜ©ņåī ņ¢ĄņĀ£ņĀ£ņØĖ Ēö╝ļéśņŖżĒģīļØ╝ņØ┤ļō£ 25 ╬╝g /mLņŚÉņä£ ņĢäļ¼┤Ļ▓āļÅä ņ▓śļ”¼ĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņØĆ ņØīņä▒ ļīĆņĪ░ĻĄ░Ļ│╝ ļ╣äĻĄÉĒĢśņŚ¼ 72%ņØś ĒģīņŖżĒåĀņŖżĒģīļĪĀņØ┤ ņĪ┤ņ×¼ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļéśĒāĆļéś ļģ╣ņ░©-ļ░żņåĪņØ┤ ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ 100 ╬╝g/mLĻ│╝ ņ£Āņé¼ĒĢ£ 5ņĢīĒīī ĒÖśņøÉ ĒÜ©ņåī ĒÖ£ņä▒ ņ¢ĄņĀ£ļŖźņØä Ļ░¢ļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŗż. ņØ┤ļŖö 5 ņĢīĒīī ĒÖśņøÉĒÜ©ņåīņØś ĒÖ£ņä▒ņØä Ļ░äņĀæņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļĪ£, ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØ┤ 5 ņĢīĒīī ĒÖśņøÉ ĒÜ©ņåīņŚÉ ņ¦üņĀæņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ▓░ĒĢ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ĒÜ©ņåīĒÖ£ņä▒ņØä ņ¢ĄņĀ£ĒĢśņśĆļŖöņ¦ĆļŖö ņĢī ņłś ņŚåļŗż. ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī, ĒÜ©ņåī ļ░śņØæņŚÉ ņ׳ņ¢┤ ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØä ņ▓śļ”¼ĒĢśņśĆņØä ļĢī, 5 ņĢīĒīī ĒÖśņøÉĒÜ©ņåīņÖĆ ļ░śņØæĒĢśļŖö ĒģīņŖżĒåĀņŖżĒģīļĪĀņØś ņ¢æņØ┤ Ļ░ÉņåīĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖĻ│Ā ļé©ņĢäņ׳ļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ│┤ņĢä ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØ┤ 5 ņĢīĒīī ĒÖśņøÉĒÜ©ņåīņØś ņ×æņÜ®ņŚÉ ņ¦üņĀæ ļśÉļŖö Ļ░äņĀæņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ņŻ╝ņŚłļŗżĻ│Ā ļ│╝ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż.
ņĄ£ĻĘ╝ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ļŖö, ņ░Ėļéśļ¼┤Ļ│╝ņŚÉ ņåŹĒĢśļŖö ņāüņłśļ”¼ļéśļ¼┤(Quercus acutissima)ņØś Ļ╗Źņ¦ł ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØ┤ 5 ņĢīĒīī ĒÖśņøÉĒÜ©ņåī ĒÖ£ņä▒ ņ¢ĄņĀ£ļŖźņØä ļéśĒāĆļé┤ļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉśņŚłļŗż(Koseki et al., 2015). ļśÉĒĢ£ ĒĢśņłśņśż(Polygonum multiflorum Thunb.) ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝Ļ│╝ ĻĘĖļĪ£ļČĆĒä░ ņ£ĀļלĒĢ£ ĒÖ£ņä▒ ņä▒ļČäņØ┤ 5 ņĢīĒīī ĒÖśņøÉĒÜ©ņåīļź╝ ņ¢ĄņĀ£ĒĢ£ļŗżļŖö ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļÅä ļ│┤Ļ│ĀļÉśņŚłļŗż(Cho et al., 2010). ļīĆļČĆļČäņØś ņ▓£ņŚ░ļ¼╝ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņØś Ļ▓ĮņÜ░, 5 ņĢīĒīī ĒÖśņøÉĒÜ©ņåī ĒÖ£ņä▒ ņ¢ĄņĀ£ņŚÉ ņ┤łņĀÉņØä ļ¦×ņČöĻ│Ā ņŚ░ĻĄ¼Ļ░Ć ņ¦äĒ¢ēļÉśņŚłņ£╝ļ®░, ņŗżņĀ£ļĪ£ ņäĖĒż ļé┤ņŚÉņä£ ņØ┤ļōżņØś ņ×æņÜ®ņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ņŚ░ĻĄ¼Ļ╣īņ¦ĆļŖö ņ¦äĒ¢ēņØ┤ ņØ┤ļŻ©ņ¢┤ņ¦Ćņ¦Ć ņĢŖĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż. ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ņŚÉņä£ļŖö ļģ╣ņ░©-ļ░żņåĪņØ┤ ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØ┤ 5 ņĢīĒīī ĒÖśņøÉĒÜ©ņåīņØś ĒÖ£ņä▒ņØä ņ¢ĄņĀ£ĒĢśņŚ¼ DHT ņāØņä▒ņØä ņ¢ĄņĀ£ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśņśĆĻ│Ā, ņØ┤ ņ×æņÜ®ņØ┤ ņŗżņĀ£ Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņäĖĒżņŚÉņä£ņØś Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņāØņä▒ņŚÉ ņ׳ņ¢┤ņä£ļÅä ĒÜ©Ļ│╝ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ×æņÜ®ĒĢ£ļŗżļŖö Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ļ│┤ņŚ¼ņŻ╝ņŚłļŗż. ņØ┤ Ļ░ÖņØĆ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļŖö, ņØ┤ņ¢┤ņ¦ĆļŖö ņ×äņāü ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ ļō▒ņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņŗżņĀ£ Ēö╝ļČĆņŚÉņä£ņØś ĒÜ©ļŖźņØ┤ ĒÖĢņØĖļÉ£ļŗżļ®┤ ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”ä ņ╣śļŻīņŚÉ ņ׳ņ¢┤ ņāłļĪ£ņÜ┤ ņ▓£ņŚ░ļ¼╝ ņåīņ×¼ļĪ£ņä£ņØś Ļ░ĆļŖźņä▒ņØä ļ│┤ņŚ¼ņżä Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒīÉļŗ©ļÉ£ļŗż.
ņé░ĒÖö ņŖżĒŖĖļĀłņŖżļŖö ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”ä ņ¦äĒ¢ēņŚÉ ņśüĒ¢źņØä ļ»Ėņ╣śĻ│Ā ļ│æļ│Ć ĒÖ£ļÅÖņØä ĒÅēĻ░ĆĒĢśļŖöļŹ░ ņ¦ĆĒæ£ļĪ£ļÅä ņé¼ņÜ®ļÉ£ļŗż(Al-Shobaili, 2014). ROSļŖö ņ£ĀņĀäņ×É ļ│ĆĒśĢĻ│╝ ņ¦Ćņ¦łņØś Ļ│╝ņé░ĒÖö, ņŚ╝ņ”Øņä▒ ņé¼ņØ┤ĒåĀņ╣┤ņØĖņØś ļČäļ╣äļź╝ ņ£ĀļÅäĒĢ£ļŗż(Briganti & Picardo, 2003). ņØ┤ļ¤¼ĒĢ£ ņØ╝ļĀ©ņØś ņ×æņÜ®ļōżņØĆ ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”ä ļ│æļ│ĆņØä ņĢģĒÖöņŗ£ĒéżļŖö ĻĖ░ņĀäņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ×æņÜ®ĒĢśļ»ĆļĪ£, ROSļź╝ ņĀ£Ļ▒░ĒĢ©ņ£╝ļĪ£ņŹ© ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”äņØä ņÖäĒÖöĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. DPPHļŖö ĒĢŁņé░ĒÖöļŖźņØä ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢśļŖö ļ░®ļ▓Ģņ£╝ļĪ£ ļØ╝ļööņ╣╝ ņåīĻ▒░ļź╝ ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ROS ņĀ£Ļ▒░ļŖźņØä ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśļŖö ņŗżĒŚśņØ┤ļ®░, ņØ┤ļź╝ ļ░öĒāĢņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒĢŁņé░ĒÖö ņŗżĒŚśņØä ņŗżņŗ£ĒĢśņśĆļŗż.
ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØś DPPH ļØ╝ļööņ╣╝ ņåīĻ▒░ļŖźņØä ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ Fig . 4ņÖĆ Ļ░Öņ£╝ļ®░, ņĢäņŖżņĮöļź┤ļĖīņé░ņØĆ ņ¢æņä▒ļīĆņĪ░ĻĄ░ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņé¼ņÜ®ļÉśņŚłļŗż. ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ ņ▓śļ”¼ ņŗ£ 1 ╬╝ g /mLņŚÉņä£ 29.23┬▒0.26%, 10 ╬╝g/mLņŚÉņä£ 86.10┬▒0.14%, 50 ╬╝g/mLņŚÉņä£ 86.90┬▒1.00%, 100 ╬╝g/mLņŚÉņä£ 86.83┬▒10.19%ņØś ļåÆņØĆ ĒĢŁņé░ĒÖöļŖźņØ┤ ņĖĪņĀĢļÉśņŚłļŗż. ņ¢æņä▒ļīĆņĪ░ĻĄ░ņØĖ ņĢäņŖżņĮöļź┤ļĖīņé░Ļ│╝ ļ╣äĻĄÉĒ¢łņØä ļĢīļÅä ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ 10 ╬╝g/mL ņØ┤ņāüņØś ņ▓śļ”¼ņĪ░Ļ▒┤ņŚÉņä£ Ļ▒░ņØś ņ£Āņé¼ĒĢ£ ĒĢŁņé░ĒÖöļŖźņØ┤ Ļ┤Ćņ░░ļÉśņŚłļŗż. ņØ┤ļŖö ņØ┤ņØĆĻ▓Į(2018)ņØś ļģ╣ņ░©ļź╝ ĒżĒĢ©ĒĢ£ ņ▓£ņŚ░ ļ│ĄĒĢ®Ēś╝ĒĢ®ļ¼╝ņØ┤ 500 ╬╝g/mLņŚÉņä£ 3 ╬╝g/mLņØś ņĢäņŖżņĮöļź┤ļĖīņé░Ļ│╝ ļ╣äņŖĘĒĢ£ ĒĢŁņé░ĒÖö ĒÜ©ļŖźņØä ļ│┤ņØĖ Ļ▓āĻ│╝ ļ╣äĻĄÉĒĢ┤ ļ│╝ ļĢī, ļģ╣ņ░©-ļ░żņåĪņØ┤ņØś ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØĆ ļŹö ļé«ņØĆ ļåŹļÅäņØĖ 10 ╬╝g/mLņŚÉņä£ 10 ╬╝g/mLņØś ņĢäņŖżņĮöļź┤ļĖīņé░Ļ│╝ ļ╣äņŖĘĒĢ£ ĒĢŁņé░ĒÖö ĒÜ©ļŖźņØä Ļ░¢ļŖö Ļ▓āņ£╝ļĪ£ ļéśĒāĆļé¼ļŗż(Lee & Jung, 2018).
ļ│Ė ņŚ░ĻĄ¼ļŖö ņ▓£ņŚ░ļ¼╝ņØĖ ļģ╣ņ░©ņÖĆ ļ░żļéśļ¼┤ņ┤ØĒżļź╝ ĒżĒĢ©ĒĢśļŖö ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØś ĒĢŁ ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”ä ĒÜ©ļŖźņØä ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”äņØś ņŻ╝ņÜöĒĢ£ ņ╣śļŻī ĻĖ░ņĀäļōżņØĖ Ļ│╝ļŗżĒĢ£ Ēö╝ņ¦ĆļČäļ╣ä ņ¢ĄņĀ£, ĒĢŁņŚ╝, 5 ņĢīĒīī ĒÖśņøÉĒÜ©ņåī ĒÖ£ņä▒ ņ¢ĄņĀ£ņÖĆ ĒĢŁņé░ĒÖöļŖźņØä ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢśņśĆļŗż. Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņäĖĒżņŚÉ ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ ņ▓śļ”¼ ņŗ£ Ēīöļ»ĖĒŖĖņé░ņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ĀļÅäļÉśļŖö Ēö╝ņ¦Ć ņāØņä▒ņØä ļåŹļÅä ņØśņĪ┤ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ░Éņåīņŗ£ņ╝░ņ£╝ļ®░ 50 ╬╝g/mL ņ▓śļ”¼ ņĪ░Ļ▒┤ņŚÉņä£ 50% ņØ┤ņāü ņ¢ĄņĀ£ĒĢśļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØĆ TLR2ņØś ĒÖ£ņä▒ņØä C. acnes CMņØä ņ▓śļ”¼ĒĢśņ¦Ć ņĢŖņØĆ ņāüĒā£ņÖĆ ļ╣äņŖĘĒĢ£ ņłśņżĆņ£╝ļĪ£Ļ╣īņ¦Ć ņ¢ĄņĀ£ĒĢśņśĆņ£╝ļ®░, ņØ┤ļŖö ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØ┤ C. acnesņØś ļÅģņä▒ņØĖņ×É ļČäļ╣äļź╝ Ļ░Éņåīņŗ£Ēé┤ņ£╝ļĪ£ņŹ© ņŚ╝ņ”Ø ļ░śņØæņØä ņ¢ĄņĀ£ĒĢśņśĆļŗżĻ│Ā ļ│╝ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. ļśÉĒĢ£ ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØ┤ 5 ņĢīĒīī ĒÖśņøÉĒÜ©ņåīņØś ĒÖ£ņä▒ņØä ņ¢ĄņĀ£ĒĢśņŚ¼ ĒģīņŖżĒåĀņŖżĒģīļĪĀņØ┤ DHTļĪ£ ņĀäĒÖśļÉśļŖö ļ░śņØæņØä 60%Ļ╣īņ¦Ć ņ¢ĄņĀ£ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ņ£╝ļ®░, 10 ╬╝g/mLņØś ļé«ņØĆ ļåŹļÅäņŚÉņä£ 80% ņØ┤ņāüņØś ļåÆņØĆ ļØ╝ļööņ╣╝ ņåīĻ▒░ļŖźļÅä ņ׳ļŗżļŖö Ļ▓āņØä ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢśņśĆļŗż. ņØ┤ļź╝ ņóģĒĢ®ĒĢ┤ ļ│╝ ļĢī, ļģ╣ņ░©ņÖĆ ļ░żņåĪņØ┤ļĪ£ ĻĄ¼ņä▒ļÉ£ ļ│ĄĒĢ®ņČöņČ£ļ¼╝ņØĆ ņ▓£ņŚ░ļ¼╝ļĪ£ņŹ© Ļ│╝ļÅäĒĢśĻ▓ī ļČäļ╣äļÉśļŖö Ēö╝ņ¦ĆņØś ņ¢ĄņĀ£, C. acnesņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ┤ ņØ╝ņ¢┤ļéśļŖö ņŚ╝ņ”Øļ░śņØæņØś ņ¢ĄņĀ£, DHT ĒĢ®ņä▒ņŚÉ Ļ┤ĆņŚ¼ĒĢśļŖö 5 ņĢīĒīī ĒÖśņøÉĒÜ©ņåī ĒÖ£ņä▒ ņ¢ĄņĀ£ņÖĆ ņ¦Ćņ¦łņØś ņé░ĒÖöļéś Ēö╝ļČĆ ņåÉņāüņØä Ļ░ĆņĀĖņśżļŖö ņ×Éņ£ĀļØ╝ļööņ╣╝ņØś ņāØņä▒ņ¢ĄņĀ£ļź╝ ĒåĄĒĢ┤ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņŚ¼ļō£ļ”ä Ēö╝ļČĆ Ļ░£ņäĀņØä ņ£äĒĢ£ ņåīņ×¼ļĪ£ ņé¼ņÜ®ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ņØä Ļ▓āņØ┤ļØ╝ ņé¼ļŻīļÉ£ļŗż.
Fig.┬Ā1.
Repression of sebum production by PEC in sebocytes. Sebocytes were cultured in various concentration (1-100 ╬╝g/mL) of PEC with 100 ╬╝M palmitic acid for 72 h. Sebum production levels were detected by nile red staining and measured using ImageJ. Scale bar is 100 ╬╝m. All results are shown as the mean ┬▒ standard deviation of triplicate data. *p < 0.05 compared to palmitic acid treated group.
Fig.┬Ā2.
Inhibition of TLR2 activity by PEC-treated C. acnes cultured media. HEK293-hTLR2 cells were treated with C. acnes cultured media or PEC-treated C. acnes cultured media for 6 h. (A) Cell viability of PEC-only treatment group was measured using MTT assay 6 h after treatment of PEC with cells. (B) Cell viability of C. acnes cultured media and PEC-treated C. acnes cultured media was measured using MTT assay 6 h after each cultured media was diluted to 1/100 and treated with cells. (C) TLR2 activity was measured by SEAP activity after 6 h of treating the cells with C. acnes cultured media and PEC-treated C. acnes cultured media in 1/100, respectively. C. acnes cultured media is a culture solution obtained by culturing only C. acnes without treating PEC, a complex extract, and PEC-treated C. acnes cultured media means a culture solution obtained by culturing C. acnes with PEC. All results are shown as the mean ┬▒ standard deviation of triplicate data. *p < 0.05 compared to C. acnes cultured medium treated group.

Fig.┬Ā3.
Reduction of 5 alpha reductase activity by PEC. The mixture containing testosterone and rat liver microsome was reacted with PEC or finasteride for 1 h. 5 alpha reductase activity was measured by detecting the remaining amount of testosterone with HPLC. All results are shown as the mean ┬▒ standard deviation of triplicate data. *p < 0.05 compared to microsome treated group.
REFERENCES
Ahn, S., Kwon, O., Lee, J. H., Kim, N., & Cha, W. S. (2013). Donguibogam: Treasured Mirror of Eastern Medicine Part VI, Miscellaneous Disorders 4. Seoul: Ministry of Health & Welfare.
Akamatsu, H., & Horio, T. (1998). The possible role of reactive oxygen species generated by neutrophils in mediating acne inflammation. Dermatology (Basel, Switzerland), 196(1), 82-85.


Al-Shobaili, H. A. (2014). Oxidants and anti-oxidants status in acne vulgaris patients with varying severity. Annals of Clinical and Laboratory Science, 44(2), 202-207.

Barrault, C., Garnier, J., Pedretti, N., Cordier-Dirikoc, S., Ratineau, E., Deguercy, A., & Bernard, F. X. (2015 Androgens induce sebaceous differentiation in sebocyte cells expressing a stable functional androgen receptor. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 34-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb. 2015.04.005.

Briganti, S., & Picardo, M. (2003). Antioxidant activity, lipid peroxidation and skin diseases. What's new. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology : JEADV, 17(6), 663-669.


Burkhart, C. N., & Burkhart, C. G. (2003). Microbiology's principle of biofilms as a major factor in the pathogenesis of acne vulgaris. International Journal of Dermatology, 42(12), 925-927.


Cho, C. H., Bae, J. S., & Kim, Y. U. (2010). 5alpha-reductase inhibitory components as antiandrogens from herbal medicine. Journal of Acupuncture and Meridian Studies, 3(2), 116-118.


Choi, C. W., Kim, Y., Kim, J. E., Seo, E. Y., Zouboulis, C. C., Kang, J. S., Youn, S. W., & Chung, J. H. (2019). Enhancement of lipid content and inflammatory cytokine secretion in SZ95 sebocytes by palmitic acid suggests a potential link between free fatty acids and acne aggravation. Experimental Dermatology, 28(2), 207-210.


Clayton, R. W., G├Čbel, K., Niessen, C. M., Paus, R., van Steensel, M., & Lim, X. (2019). Homeostasis of the sebaceous gland and mechanisms of acne pathogenesis. The British Journal of Dermatology, 181(4), 677-690.


Cong, T. X., Hao, D., Wen, X., Li, X. H., He, G., & Jiang, X. (2019). From pathogenesis of acne vulgaris to anti-acne agents. Archives of Dermatological Research, 311(5), 337-349.


Forester, S. C., & Lambert, J. D. (2011). The role of antioxidant versus pro-oxidant effects of green tea polyphenols in cancer prevention. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 55(6), 844-854.


Hazarika, N. (2021). Acne vulgaris: new evidence in pathogenesis and future modalities of treatment. The Journal of Dermatological Treatment, 32(3), 277-285.


Im, M., Kim, S. Y., Sohn, K. C., Choi, D. K., Lee, Y., Seo, Y. J., Kim, C. D., Hwang, Y. L., Zouboulis, C. C., & Lee, J. H. (2012). Epigallocatechin-3-gallate suppresses IGF-I-induced lipogenesis and cytokine expression in SZ95 sebocytes. The Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 132(12), 2700-2708.


Kawasaki, T., & Kawai, T. (2014 Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Frontiers in Immunology, 5:461.doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00461.


Kim, J. Y., Kim, S. Y., Kwon, H. M., Kim, C. H., Lee, S. J., Park, S. C., & Kim, K. H. (2014). Comparison of Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activity on Chestnut, Chestnut Shell and Leaves of Castanea crenata Extracts. Korean Journal of Medicinal Crop Science, 22(1), 8-16.

Koseki, J., Matsumoto, T., Matsubara, Y., Tsuchiya, K., Mizuhara, Y., Sekiguchi, K., Nishimura, H., Watanabe, J., Kaneko, A., Hattori, T., Maemura, K., & Kase, Y. (2015 Inhibition of Rat 5╬▒-Reductase Activity and Testosterone-Induced Sebum Synthesis in Hamster Sebocytes by an Extract of Quercus acutissima Cortex. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine : eCAM, (2015 853846.doi: 10.1155/2015/853846.



Kurokawa, I., Danby, F. W., Ju, Q., Wang, X., Xiang, L. F., Xia, L., Chen, W., Nagy, I., Picardo, M., Suh, D. H., Ganceviciene, R., Schagen, S., Tsatsou, F., & Zouboulis, C. C. (2009). New developments in our understanding of acne pathogenesis and treatment. Experimental Dermatology, 18(10), 821-832.


Lai, J. J., Chang, P., Lai, K. P., Chen, L., & Chang, C. (2012). The role of androgen and androgen receptor in skin-related disorders. Archives of dermatological research, 304(7), 499-510.



Lee, E. H., Hong, S. H., & Cho, Y. J. (2017). Biological Activities of Extracts from Okkwang (Castanea crenata) Chestnut Bur. Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition, 46(5), 572-580.

Lee, E. K., & Jung, S. H. (2018). Anti-inflammatory and Anti-oxidant effect of Natural Herbs Mixture in RAW264.7 Cell Line. Journal of the Korean Society of Cosmetology, 24(1), 42-50.
Li, X., He, C., Chen, Z., Zhou, C., Gan, Y., & Jia, Y. (2017). A review of the role of sebum in the mechanism of acne pathogenesis. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 16(2), 168-173.


Makrantonaki, E., Ganceviciene, R., & Zouboulis, C. (2011). An update on the role of the sebaceous gland in the pathogenesis of acne. Dermato-endocrinology, 3(1), 41-49.



Sanchez, C., & Keri, J. (2022 Androgen Receptor Inhibitors in the Treatment of Acne Vulgaris: Efficacy and Safety Profiles of Clascoterone 1% Cream. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology, 15:1357-1366. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S289750.



Saric, S., Notay, M., & Sivamani, R. K. (2016 Green Tea and Other Tea Polyphenols: Effects on Sebum Production and Acne Vulgaris. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland), 6(1), 2.doi: 10.3390/antiox6010002.



Sato, T., Akimoto, N., Kitamura, K., Kurihara, H., Hayashi, N., & Ito, A. (2013). Adapalene suppresses sebum accumulation via the inhibition of triacylglycerol biosynthesis and perilipin expression in differentiated hamster sebocytes in vitro. Journal of Dermatological Science, 70(3), 204-210.


Williams, H. C., Dellavalle, R. P., & Garner, S. (2012). Acne vulgaris. The Lancet, 379(9813), 361-372.

Yoon, J. Y., Kwon, H. H., Min, S. U., Thiboutot, D. M., & Suh, D. H. (2013). Epigallocatechin-3-gallate improves acne in humans by modulating intracellular molecular targets and inhibiting P. acnes. The Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 133(2), 429-440.


- TOOLS



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print